Two-Staged Acoustic Modeling Adaption for Robust Speech Recognition by the Example of German Oral History Interviews
Paper and Code
Aug 19, 2019


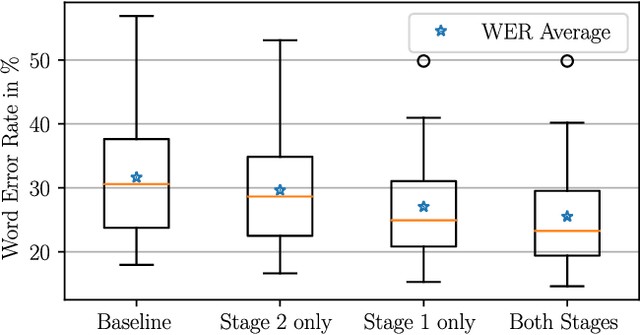
In automatic speech recognition, often little training data is available for specific challenging tasks, but training of state-of-the-art automatic speech recognition systems requires large amounts of annotated speech. To address this issue, we propose a two-staged approach to acoustic modeling that combines noise and reverberation data augmentation with transfer learning to robustly address challenges such as difficult acoustic recording conditions, spontaneous speech, and speech of elderly people. We evaluate our approach using the example of German oral history interviews, where a relative average reduction of the word error rate by 19.3% is achieved.
* IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME),
Shanghai, China, July 2019 * Accepted for IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo
(ICME), Shanghai, China, July 2019
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge