Two-Leg Deep Space Relay Architectures: Performance, Challenges, and Perspectives
Paper and Code
May 27, 2022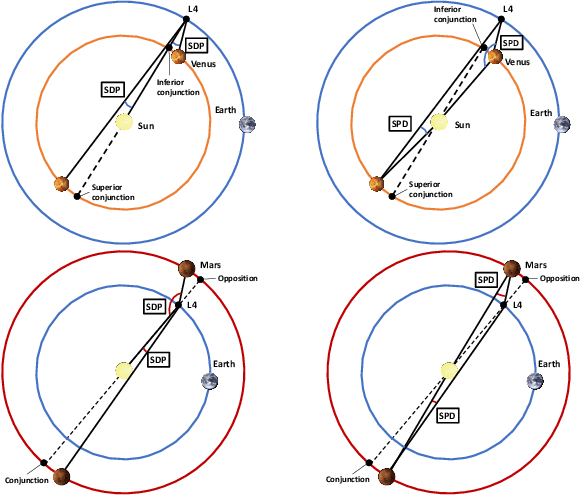
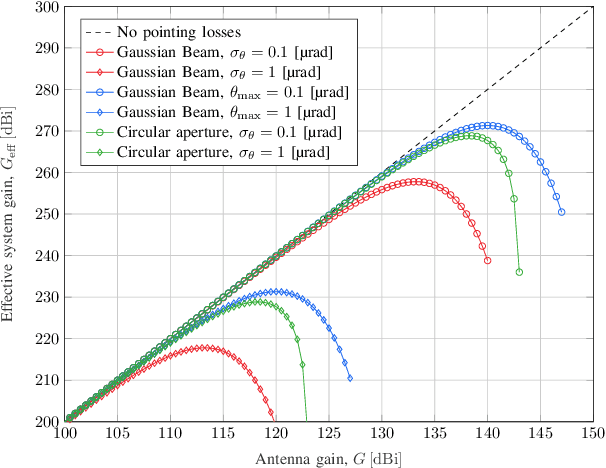
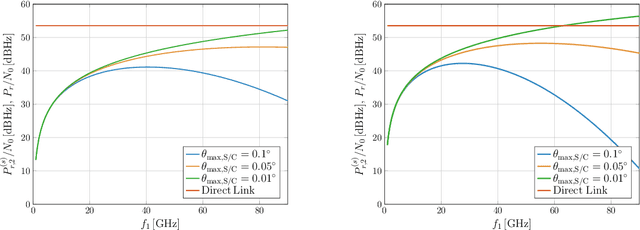
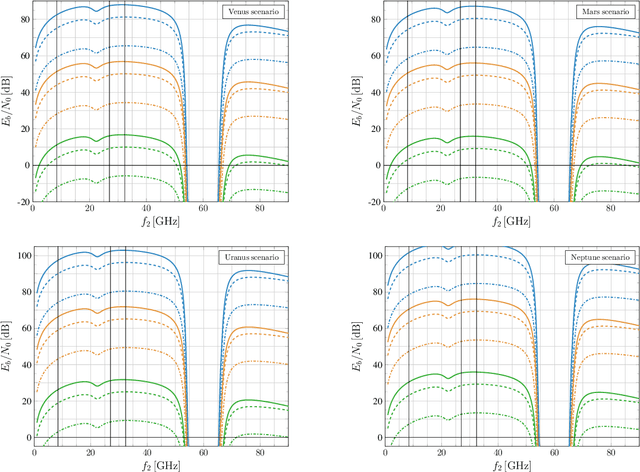
In this paper, architectures for interplanetary communications that feature the use of a data relay are investigated. In the considered "two-leg" architecture, a spacecraft orbiting the Earth, or in orbit at a Lagrange point, receives data from a deep space probe (leg-1) and relays them towards ground (leg-2). Different wireless technologies for the interplanetary link, namely, radio frequencies above the Ka band and optical frequencies, are considered. Moreover, the cases of transparent and regenerative relaying as well as different different orbital configurations are addressed, offering a thorough analysis of such systems from different viewpoints. Results show that, under certain constraints in terms of pointing accuracy and onboard antenna size, the adoption of a two-leg architecture can achieve the data rates supported by direct space-to-Earth link configurations with remarkably smaller ground station antennas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge