Twin Augmented Architectures for Robust Classification of COVID-19 Chest X-Ray Images
Paper and Code
Feb 16, 2021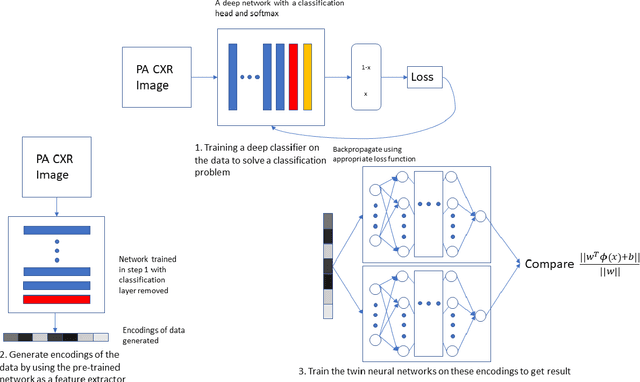
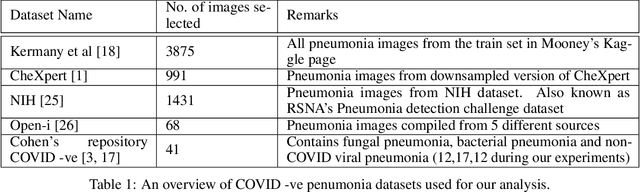
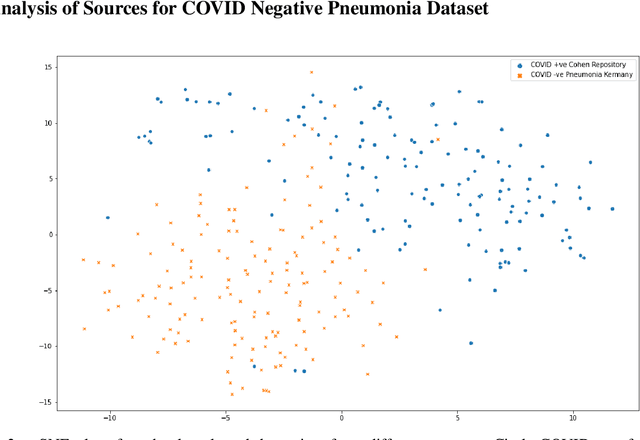
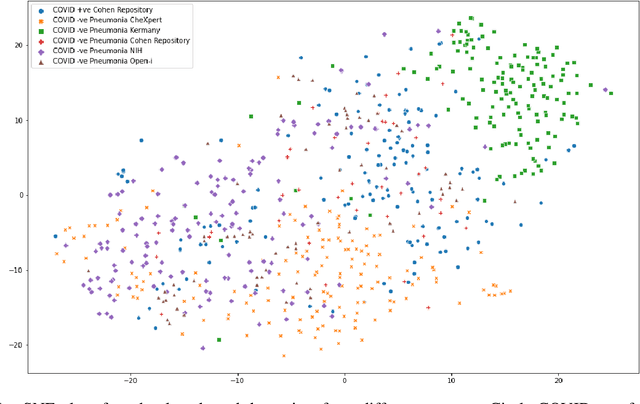
The gold standard for COVID-19 is RT-PCR, testing facilities for which are limited and not always optimally distributed. Test results are delayed, which impacts treatment. Expert radiologists, one of whom is a co-author, are able to diagnose COVID-19 positivity from Chest X-Rays (CXR) and CT scans, that can facilitate timely treatment. Such diagnosis is particularly valuable in locations lacking radiologists with sufficient expertise and familiarity with COVID-19 patients. This paper has two contributions. One, we analyse literature on CXR based COVID-19 diagnosis. We show that popular choices of dataset selection suffer from data homogeneity, leading to misleading results. We compile and analyse a viable benchmark dataset from multiple existing heterogeneous sources. Such a benchmark is important for realistically testing models. Our second contribution relates to learning from imbalanced data. Datasets for COVID X-Ray classification face severe class imbalance, since most subjects are COVID -ve. Twin Support Vector Machines (Twin SVM) and Twin Neural Networks (Twin NN) have, in recent years, emerged as effective ways of handling skewed data. We introduce a state-of-the-art technique, termed as Twin Augmentation, for modifying popular pre-trained deep learning models. Twin Augmentation boosts the performance of a pre-trained deep neural network without requiring re-training. Experiments show, that across a multitude of classifiers, Twin Augmentation is very effective in boosting the performance of given pre-trained model for classification in imbalanced settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge