TUM-VIE: The TUM Stereo Visual-Inertial Event Dataset
Paper and Code
Aug 16, 2021
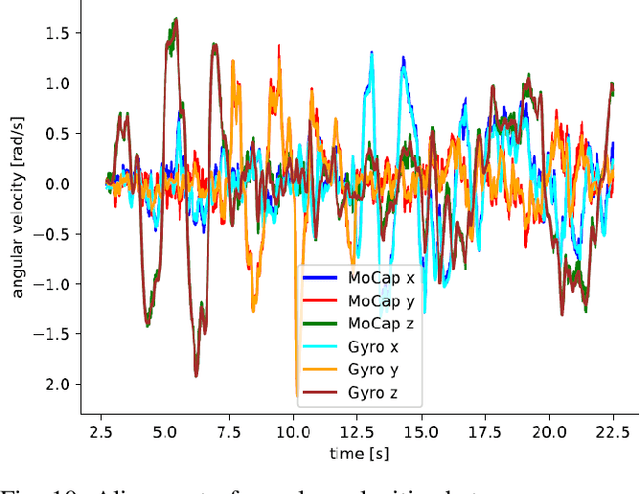
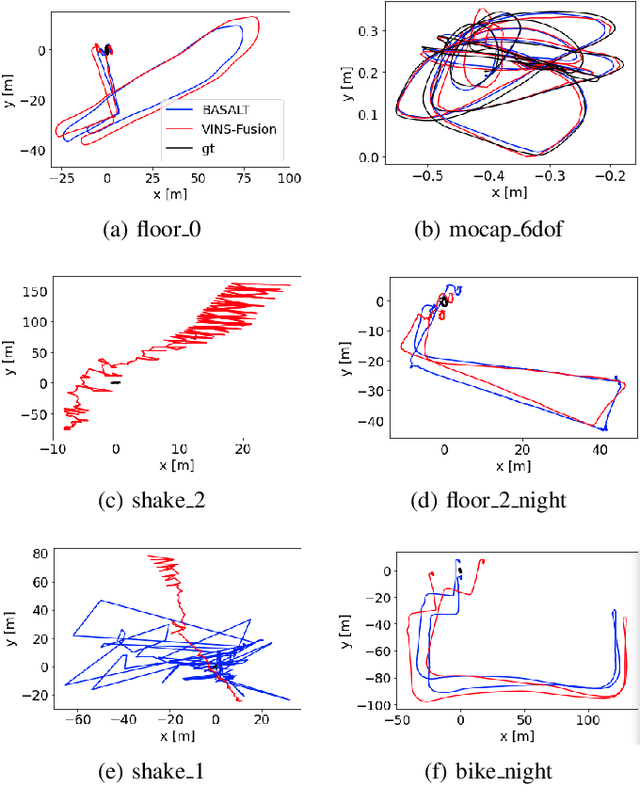
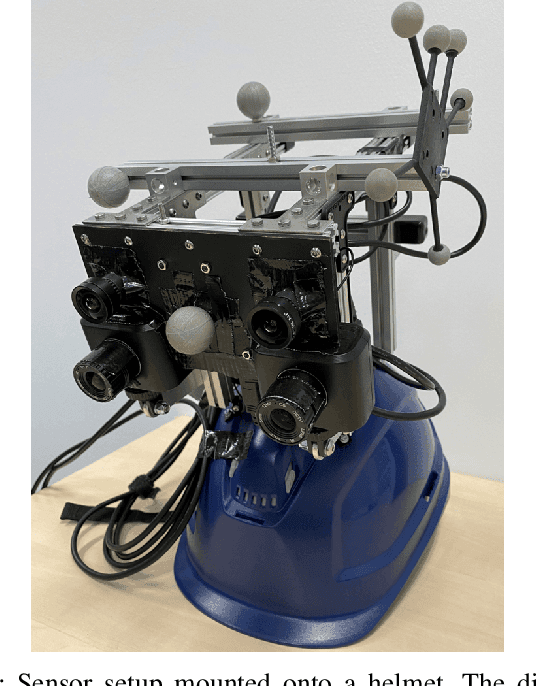
Event cameras are bio-inspired vision sensors which measure per pixel brightness changes. They offer numerous benefits over traditional, frame-based cameras, including low latency, high dynamic range, high temporal resolution and low power consumption. Thus, these sensors are suited for robotics and virtual reality applications. To foster the development of 3D perception and navigation algorithms with event cameras, we present the TUM-VIE dataset. It consists of a large variety of handheld and head-mounted sequences in indoor and outdoor environments, including rapid motion during sports and high dynamic range scenarios. The dataset contains stereo event data, stereo grayscale frames at 20Hz as well as IMU data at 200Hz. Timestamps between all sensors are synchronized in hardware. The event cameras contain a large sensor of 1280x720 pixels, which is significantly larger than the sensors used in existing stereo event datasets (at least by a factor of ten). We provide ground truth poses from a motion capture system at 120Hz during the beginning and end of each sequence, which can be used for trajectory evaluation. TUM-VIE includes challenging sequences where state-of-the art visual SLAM algorithms either fail or result in large drift. Hence, our dataset can help to push the boundary of future research on event-based visual-inertial perception algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge