TS-OOD: Evaluating Time-Series Out-of-Distribution Detection and Prospective Directions for Progress
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2025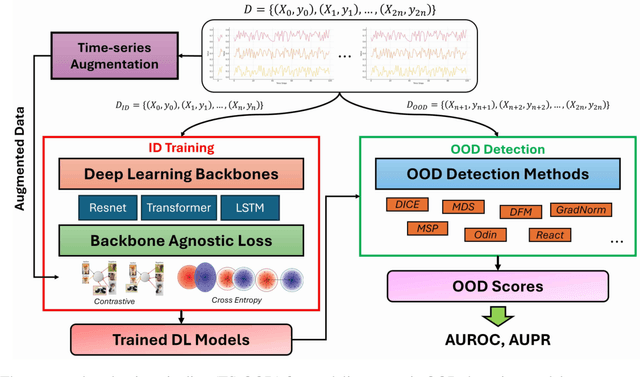
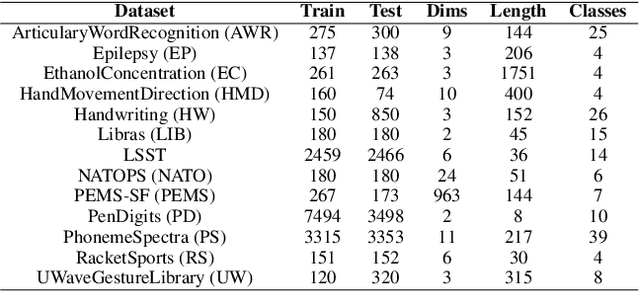
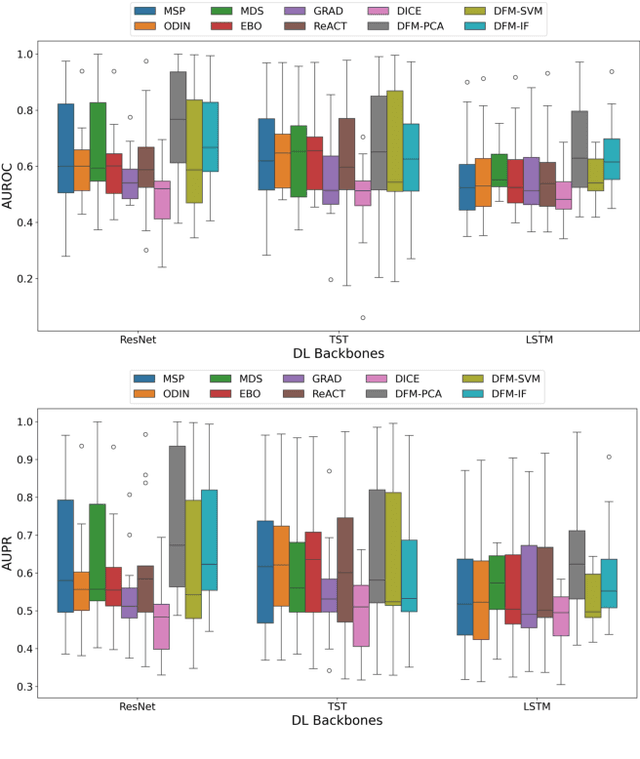
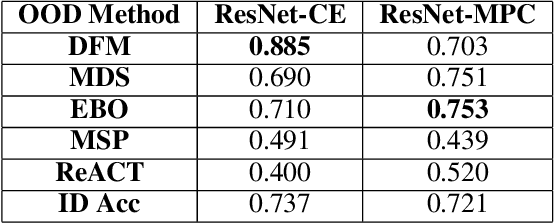
Detecting out-of-distribution (OOD) data is a fundamental challenge in the deployment of machine learning models. From a security standpoint, this is particularly important because OOD test data can result in misleadingly confident yet erroneous predictions, which undermine the reliability of the deployed model. Although numerous models for OOD detection have been developed in computer vision and language, their adaptability to the time-series data domain remains limited and under-explored. Yet, time-series data is ubiquitous across manufacturing and security applications for which OOD is essential. This paper seeks to address this research gap by conducting a comprehensive analysis of modality-agnostic OOD detection algorithms. We evaluate over several multivariate time-series datasets, deep learning architectures, time-series specific data augmentations, and loss functions. Our results demonstrate that: 1) the majority of state-of-the-art OOD methods exhibit limited performance on time-series data, and 2) OOD methods based on deep feature modeling may offer greater advantages for time-series OOD detection, highlighting a promising direction for future time-series OOD detection algorithm development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge