Trip Recovery in Lower-Limb Prostheses using Reachable Sets of Predicted Human Motion
Paper and Code
Oct 21, 2020
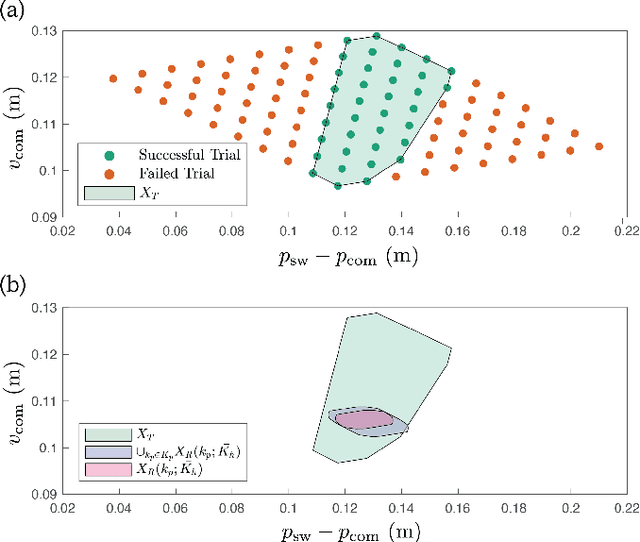
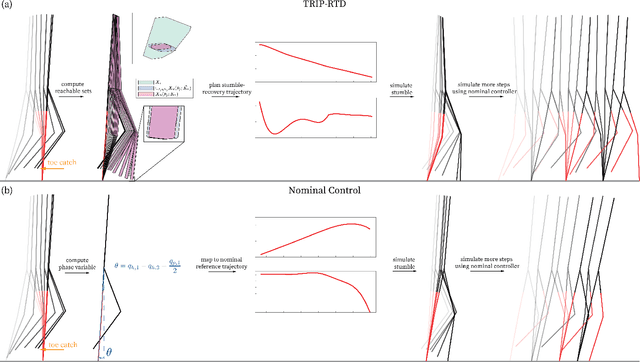
People with lower-limb loss, the majority of which use passive prostheses, exhibit a high incidence of falls each year. Powered lower-limb prostheses have the potential to reduce fall rates by actively helping the user recover from a stumble, but the unpredictability of the human response makes it difficult to design controllers that ensure a successful recovery. This paper presents a method called TRIP-RTD (Trip Recovery in Prostheses via Reachability-based Trajectory Design) for online trajectory planning in a knee prosthesis during and after a stumble that can accommodate a set of possible predictions of human behavior. Using this predicted set of human behavior, the proposed method computes a parameterized reachable set of trajectories for the human-prosthesis system. To ensure safety at run-time, TRIP-RTD selects a trajectory for the prosthesis that guarantees that all possible states of the human-prosthesis system at touchdown arrive in the basin of attraction of the nominal behavior of the system. In simulated stumble experiments where a nominal phase-based controller was unable to help the system recover, TRIP-RTD produced trajectories in under 101 ms that led to successful recoveries for all feasible solutions found.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge