Trinity of Pixel Enhancement: a Joint Solution for Demosaicking, Denoising and Super-Resolution
Paper and Code
May 07, 2019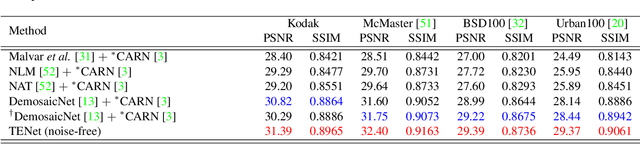
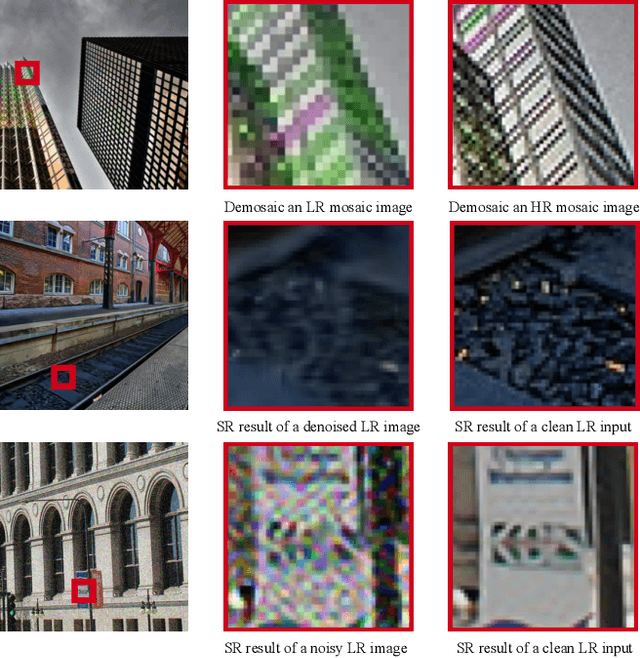
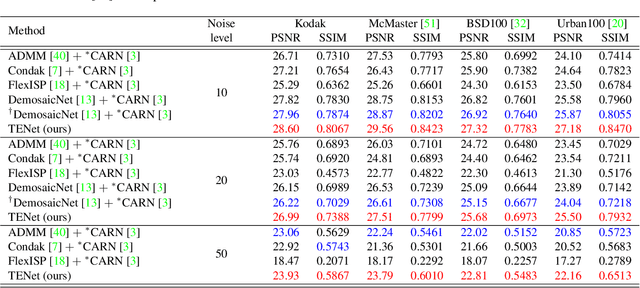
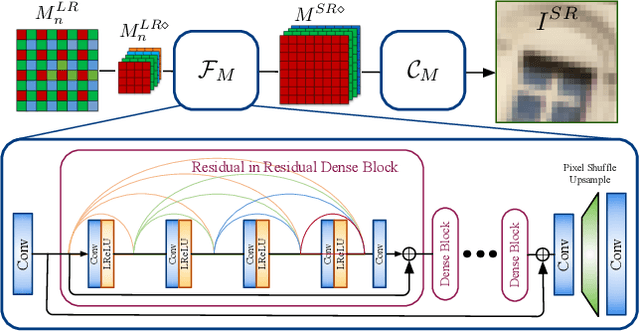
Demosaicing, denoising and super-resolution (SR) are of practical importance in digital image processing and have been studied independently in the passed decades. Despite the recent improvement of learning-based image processing methods in image quality, there lacks enough analysis into their interactions and characteristics under a realistic setting of the mixture problem of demosaicing, denoising and SR. In existing solutions, these tasks are simply combined to obtain a high-resolution image from a low-resolution raw mosaic image, resulting in a performance drop of the final image quality. In this paper, we first rethink the mixture problem from a holistic perspective and then propose the Trinity Enhancement Network (TENet), a specially designed learning-based method for the mixture problem, which adopts a novel image processing pipeline order and a joint learning strategy. In order to obtain the correct color sampling for training, we also contribute a new dataset namely PixelShift200, which consists of high-quality full color sampled real-world images using the advanced pixel shift technique. Experiments demonstrate that our TENet is superior to existing solutions in both quantitative and qualitative perspective. Our experiments also show the necessity of the proposed PixelShift200 dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge