TReR: A Lightweight Transformer Re-Ranking Approach for 3D LiDAR Place Recognition
Paper and Code
May 29, 2023


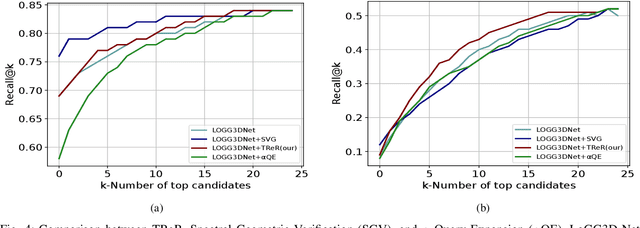
Autonomous driving systems often require reliable loop closure detection to guarantee reduced localization drift. Recently, 3D LiDAR-based localization methods have used retrieval-based place recognition to find revisited places efficiently. However, when deployed in challenging real-world scenarios, the place recognition models become more complex, which comes at the cost of high computational demand. This work tackles this problem from an information-retrieval perspective, adopting a first-retrieve-then-re-ranking paradigm, where an initial loop candidate ranking, generated from a 3D place recognition model, is re-ordered by a proposed lightweight transformer-based re-ranking approach (TReR). The proposed approach relies on global descriptors only, being agnostic to the place recognition model. The experimental evaluation, conducted on the KITTI Odometry dataset, where we compared TReR with s.o.t.a. re-ranking approaches such as alphaQE and SGV, indicate the robustness and efficiency when compared to alphaQE while offering a good trade-off between robustness and efficiency when compared to SGV.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge