Training Neural Machine Translation using Word Embedding-based Loss
Paper and Code
Jul 30, 2018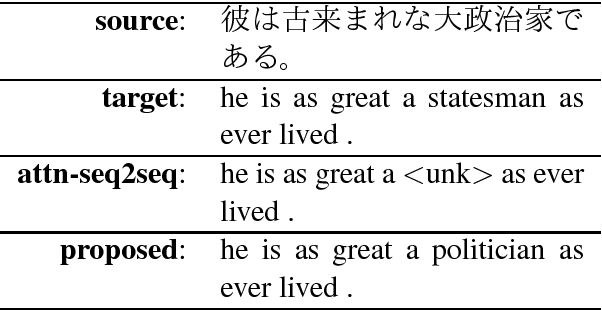
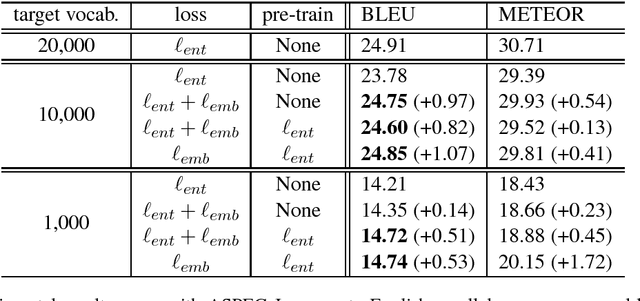
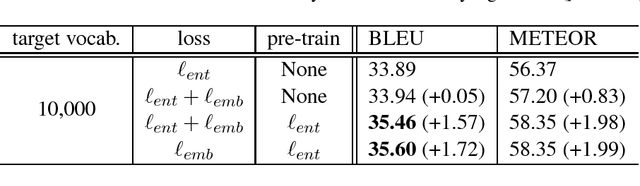
In neural machine translation (NMT), the computational cost at the output layer increases with the size of the target-side vocabulary. Using a limited-size vocabulary instead may cause a significant decrease in translation quality. This trade-off is derived from a softmax-based loss function that handles in-dictionary words independently, in which word similarity is not considered. In this paper, we propose a novel NMT loss function that includes word similarity in forms of distances in a word embedding space. The proposed loss function encourages an NMT decoder to generate words close to their references in the embedding space; this helps the decoder to choose similar acceptable words when the actual best candidates are not included in the vocabulary due to its size limitation. In experiments using ASPEC Japanese-to-English and IWSLT17 English-to-French data sets, the proposed method showed improvements against a standard NMT baseline in both datasets; especially with IWSLT17 En-Fr, it achieved up to +1.72 in BLEU and +1.99 in METEOR. When the target-side vocabulary was very limited to 1,000 words, the proposed method demonstrated a substantial gain, +1.72 in METEOR with ASPEC Ja-En.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge