Training generative networks using random discriminators
Paper and Code
Apr 22, 2019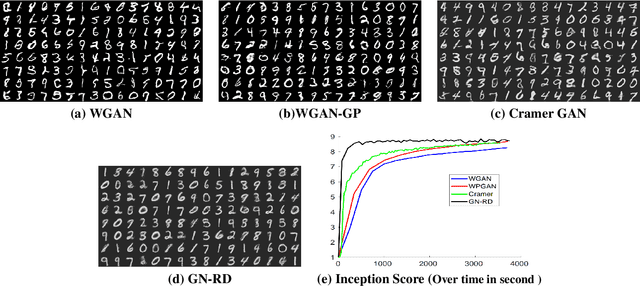

In recent years, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) have drawn a lot of attentions for learning the underlying distribution of data in various applications. Despite their wide applicability, training GANs is notoriously difficult. This difficulty is due to the min-max nature of the resulting optimization problem and the lack of proper tools of solving general (non-convex, non-concave) min-max optimization problems. In this paper, we try to alleviate this problem by proposing a new generative network that relies on the use of random discriminators instead of adversarial design. This design helps us to avoid the min-max formulation and leads to an optimization problem that is stable and could be solved efficiently. The performance of the proposed method is evaluated using handwritten digits (MNIST) and Fashion products (Fashion-MNIST) data sets. While the resulting images are not as sharp as adversarial training, the use of random discriminator leads to a much faster algorithm as compared to the adversarial counterpart. This observation, at the minimum, illustrates the potential of the random discriminator approach for warm-start in training GANs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge