Training a code-switching language model with monolingual data
Paper and Code
Nov 14, 2019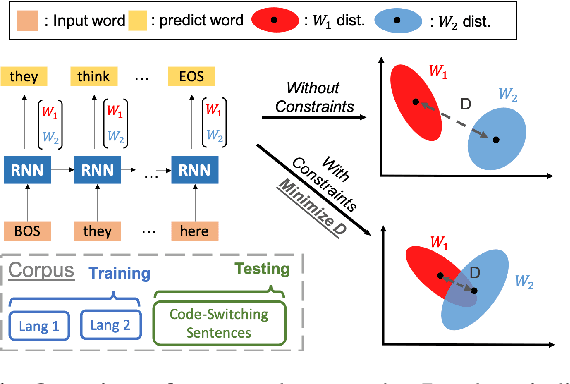
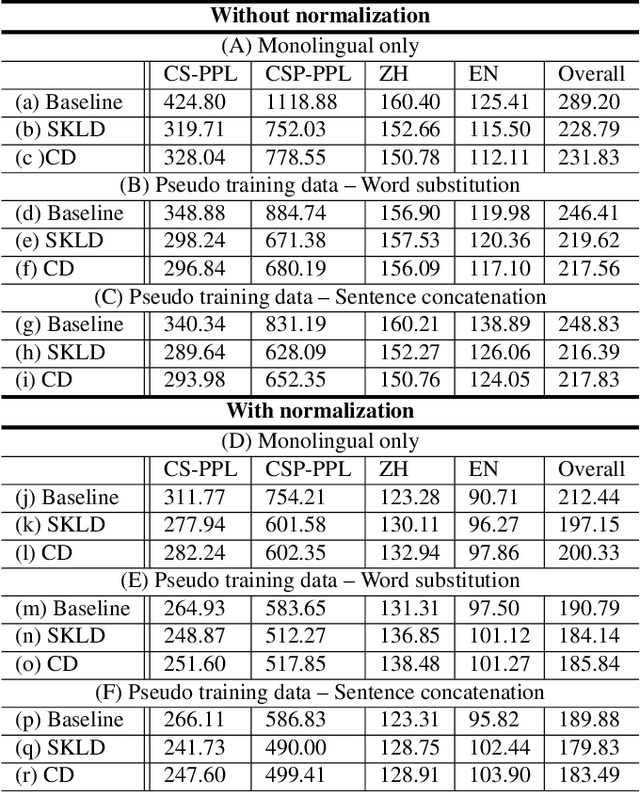
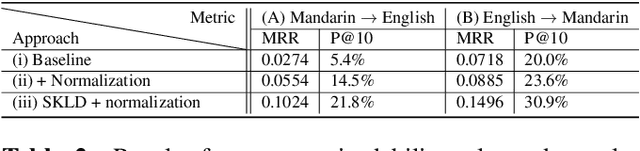
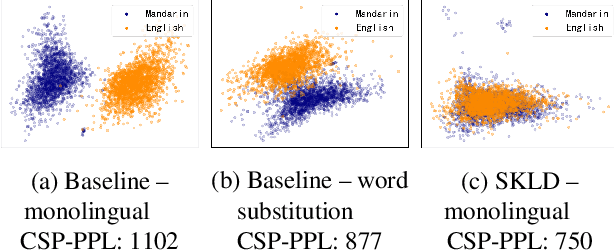
A lack of code-switching data complicates the training of code-switching (CS) language models. We propose an approach to train such CS language models on monolingual data only. By constraining and normalizing the output projection matrix in RNN-based language models, we bring embeddings of different languages closer to each other. Numerical and visualization results show that the proposed approaches remarkably improve the performance of CS language models trained on monolingual data. The proposed approaches are comparable or even better than training CS language models with artificially generated CS data. We additionally use unsupervised bilingual word translation to analyze whether semantically equivalent words in different languages are mapped together.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge