TRACE: Early Detection of Chronic Kidney Disease Onset with Transformer-Enhanced Feature Embedding
Paper and Code
Dec 03, 2020
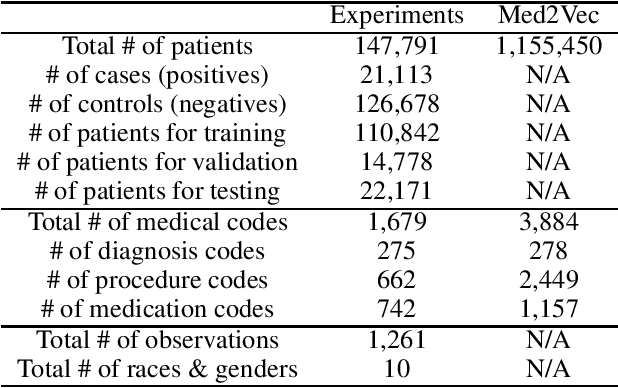
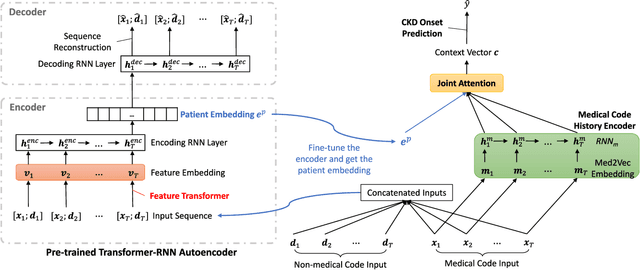
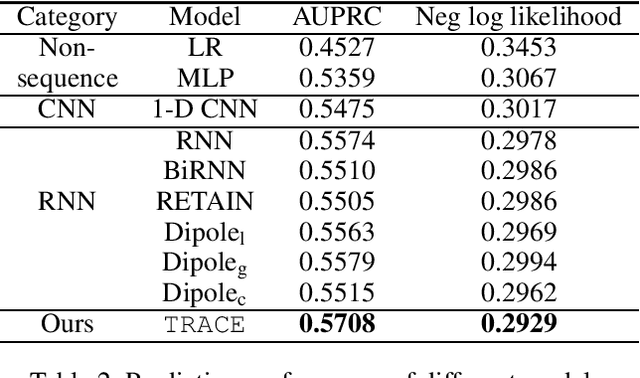
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has a poor prognosis due to excessive risk factors and comorbidities associated with it. The early detection of CKD faces challenges of insufficient medical histories of positive patients and complicated risk factors. In this paper, we propose the TRACE (Transformer-RNN Autoencoder-enhanced CKD Detector) framework, an end-to-end prediction model using patients' medical history data, to deal with these challenges. TRACE presents a comprehensive medical history representation with a novel key component: a Transformer-RNN autoencoder. The autoencoder jointly learns a medical concept embedding via Transformer for each hospital visit, and a latent representation which summarizes a patient's medical history across all the visits. We compared TRACE with multiple state-of-the-art methods on a dataset derived from real-world medical records. Our model has achieved 0.5708 AUPRC with a 2.31% relative improvement over the best-performing method. We also validated the clinical meaning of the learned embeddings through visualizations and a case study, showing the potential of TRACE to serve as a general disease prediction model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge