Towards the Practical Utility of Federated Learning in the Medical Domain
Paper and Code
Jul 14, 2022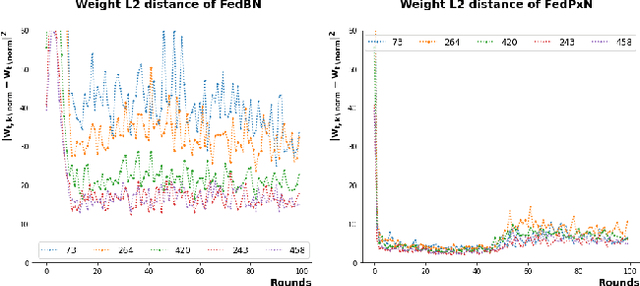
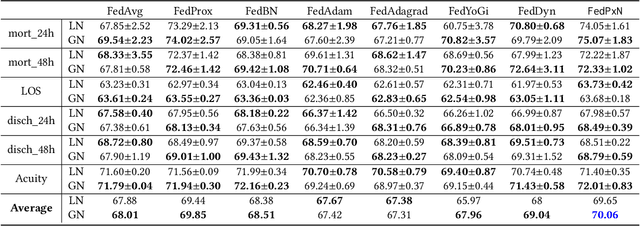
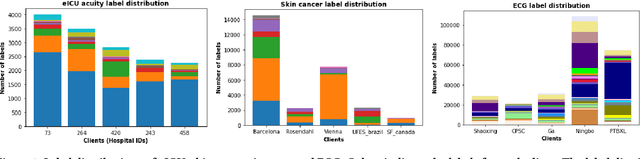
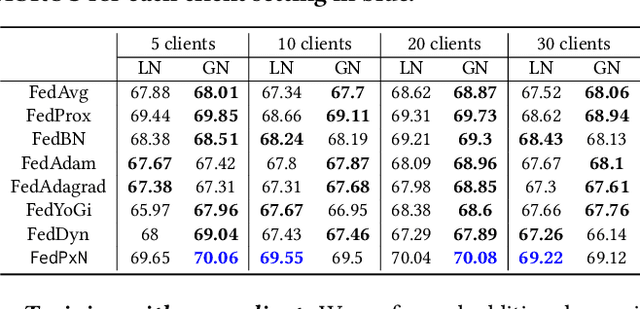
Federated learning (FL) is an active area of research. One of the most suitable areas for adopting FL is the medical domain, where patient privacy must be respected. Previous research, however, does not fully consider who will most likely use FL in the medical domain. It is not the hospitals who are eager to adopt FL, but the service providers such as IT companies who want to develop machine learning models with real patient records. Moreover, service providers would prefer to focus on maximizing the performance of the models at the lowest cost possible. In this work, we propose empirical benchmarks of FL methods considering both performance and monetary cost with three real-world datasets: electronic health records, skin cancer images, and electrocardiogram datasets. We also propose Federated learning with Proximal regularization eXcept local Normalization (FedPxN), which, using a simple combination of FedProx and FedBN, outperforms all other FL algorithms while consuming only slightly more power than the most power efficient method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge