Towards Safer Self-Driving Through Great PAIN
Paper and Code
Mar 24, 2020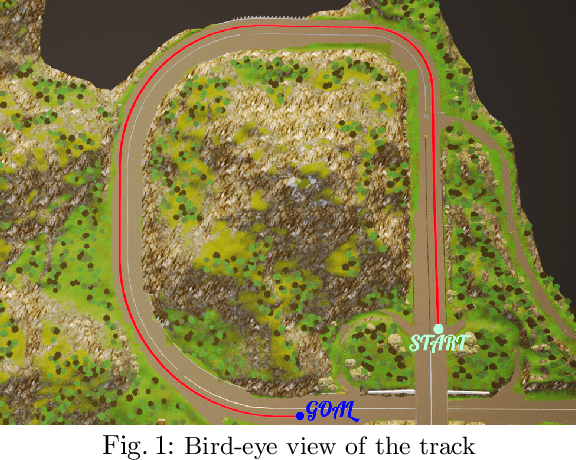
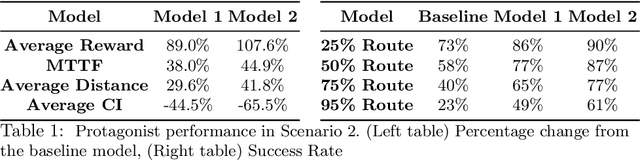
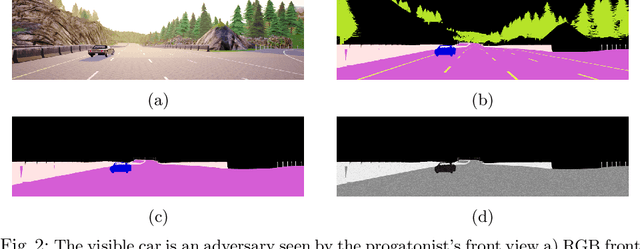
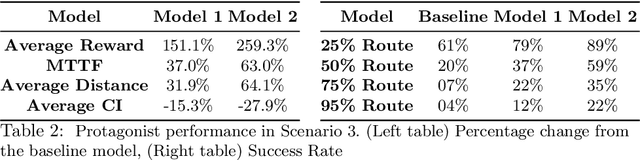
Automated vehicles' neural networks suffer from overfit, poor generalizability, and untrained edge cases due to limited data availability. Researchers synthesize randomized edge-case scenarios to assist in the training process, though simulation introduces potential for overfit to latent rules and features. Automating worst-case scenario generation could yield informative data for improving self driving. To this end, we introduce a "Physically Adversarial Intelligent Network" (PAIN), wherein self-driving vehicles interact aggressively in the CARLA simulation environment. We train two agents, a protagonist and an adversary, using dueling double deep Q networks (DDDQNs) with prioritized experience replay. The coupled networks alternately seek-to-collide and to avoid collisions such that the "defensive" avoidance algorithm increases the mean-time-to-failure and distance traveled under non-hostile operating conditions. The trained protagonist becomes more resilient to environmental uncertainty and less prone to corner case failures resulting in collisions than the agent trained without an adversary.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge