Towards Proper Contrastive Self-supervised Learning Strategies For Music Audio Representation
Paper and Code
Jul 10, 2022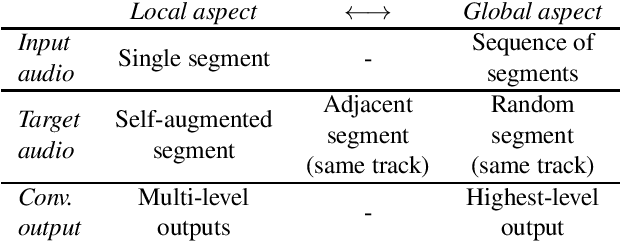
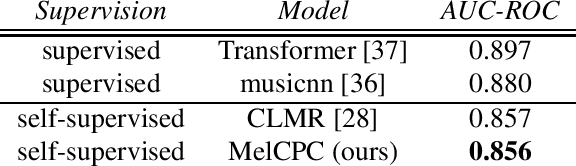
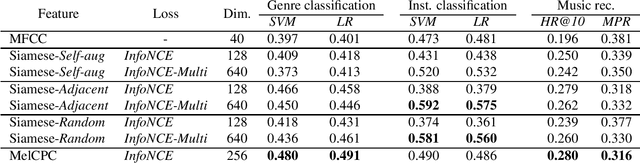
The common research goal of self-supervised learning is to extract a general representation which an arbitrary downstream task would benefit from. In this work, we investigate music audio representation learned from different contrastive self-supervised learning schemes and empirically evaluate the embedded vectors on various music information retrieval (MIR) tasks where different levels of the music perception are concerned. We analyze the results to discuss the proper direction of contrastive learning strategies for different MIR tasks. We show that these representations convey a comprehensive information about the auditory characteristics of music in general, although each of the self-supervision strategies has its own effectiveness in certain aspect of information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge