Towards practical object detection for weed spraying in precision agriculture
Paper and Code
Sep 22, 2021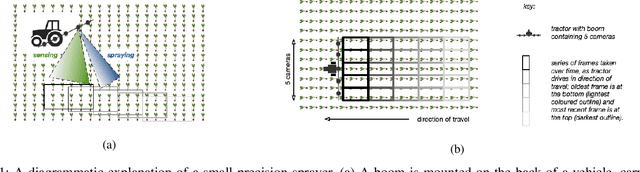

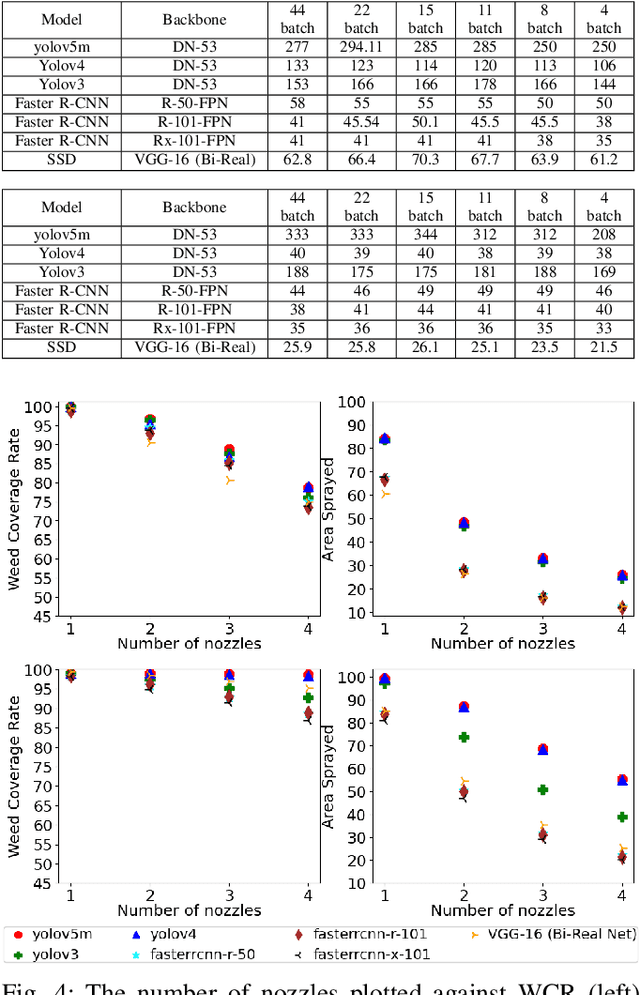
The evolution of smaller, faster processors and cheaper digital storage mechanisms across the last 4-5 decades has vastly increased the opportunity to integrate intelligent technologies in a wide range of practical environments to address a broad spectrum of tasks. One exciting application domain for such technologies is precision agriculture, where the ability to integrate on-board machine vision with data-driven actuation means that farmers can make decisions about crop care and harvesting at the level of the individual plant rather than the whole field. This makes sense both economically and environmentally. However, the key driver for this capability is fast and robust machine vision -- typically driven by machine learning (ML) solutions and dependent on accurate modelling. One critical challenge is that the bulk of ML-based vision research considers only metrics that evaluate the accuracy of object detection and do not assess practical factors. This paper introduces three metrics that highlight different aspects relevant for real-world deployment of precision weeding and demonstrates their utility through experimental results.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge