Towards Machine Comprehension of Spoken Content: Initial TOEFL Listening Comprehension Test by Machine
Paper and Code
Aug 23, 2016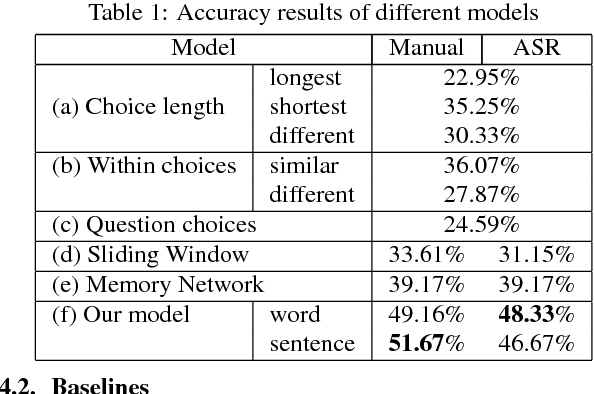
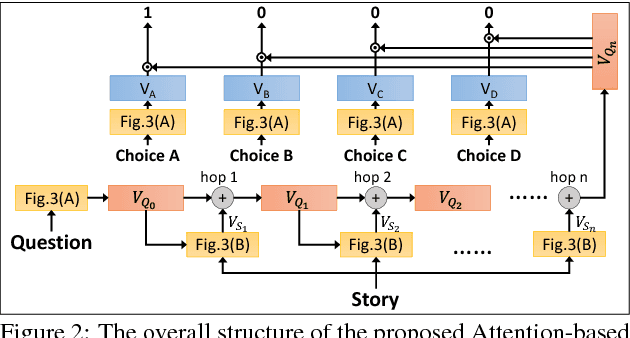
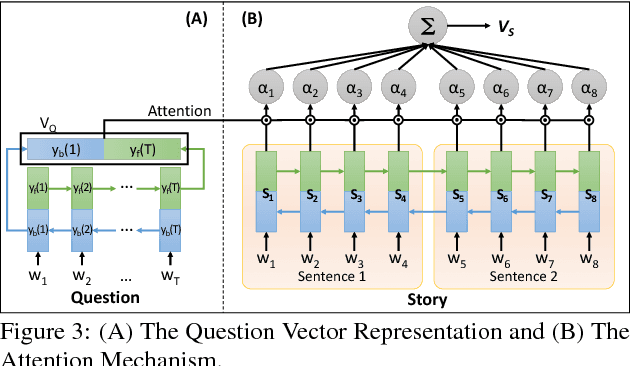

Multimedia or spoken content presents more attractive information than plain text content, but it's more difficult to display on a screen and be selected by a user. As a result, accessing large collections of the former is much more difficult and time-consuming than the latter for humans. It's highly attractive to develop a machine which can automatically understand spoken content and summarize the key information for humans to browse over. In this endeavor, we propose a new task of machine comprehension of spoken content. We define the initial goal as the listening comprehension test of TOEFL, a challenging academic English examination for English learners whose native language is not English. We further propose an Attention-based Multi-hop Recurrent Neural Network (AMRNN) architecture for this task, achieving encouraging results in the initial tests. Initial results also have shown that word-level attention is probably more robust than sentence-level attention for this task with ASR errors.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge