Towards Efficient Compressive Data Collection in the Internet of Things
Paper and Code
May 29, 2021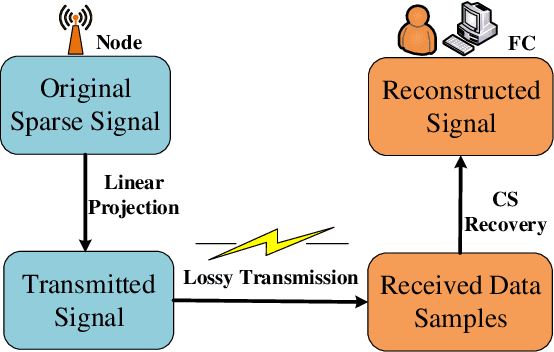
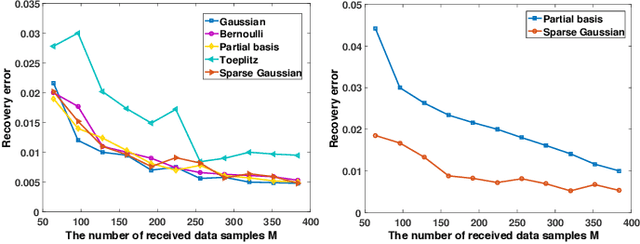
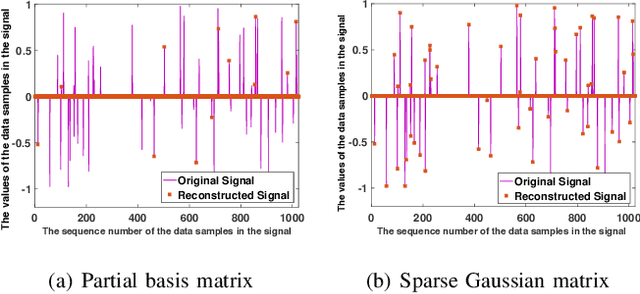
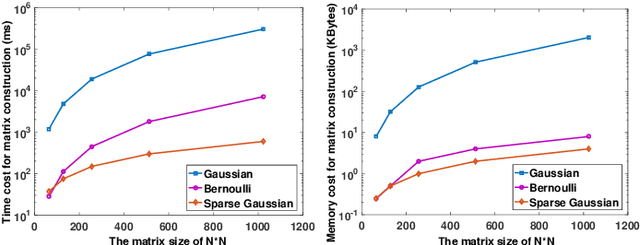
It is of paramount importance to achieve efficient data collection in the Internet of Things (IoT). Due to the inherent structural properties (e.g., sparsity) existing in many signals of interest, compressive sensing (CS) technology has been extensively used for data collection in IoT to improve both accuracy and energy efficiency. Apart from the existing works which leverage CS as a channel coding scheme to deal with data loss during transmission, some recent results have started to employ CS as a source coding strategy. The frequently used projection matrices in these CS-based source coding schemes include dense random matrices (e.g., Gaussian matrices or Bernoulli matrices) and structured matrices (e.g., Toeplitz matrices). However, these matrices are either difficult to be implemented on resource-constrained IoT sensor nodes or have limited applicability. To address these issues, in this paper, we design a novel simple and efficient projection matrix, named sparse Gaussian matrix, which is easy and resource-saving to be implemented in practical IoT applications. We conduct both theoretical analysis and experimental evaluation of the designed sparse Gaussian matrix. The results demonstrate that employing the designed projection matrix to perform CS-based source coding could significantly save time and memory cost while ensuring satisfactory signal recovery performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge