Towards a distributed and real-time framework for robots: Evaluation of ROS 2.0 communications for real-time robotic applications
Paper and Code
Sep 07, 2018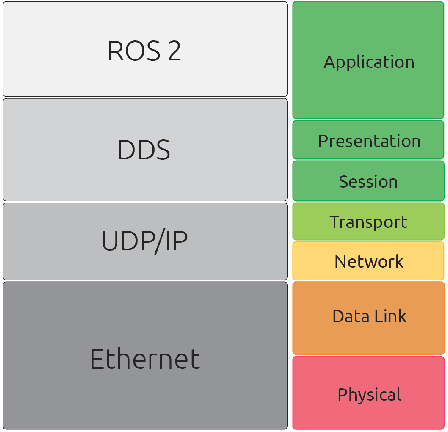
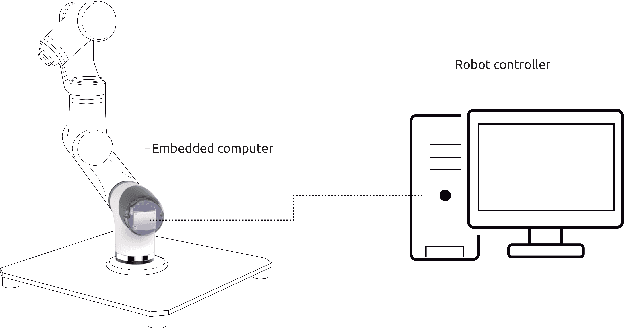
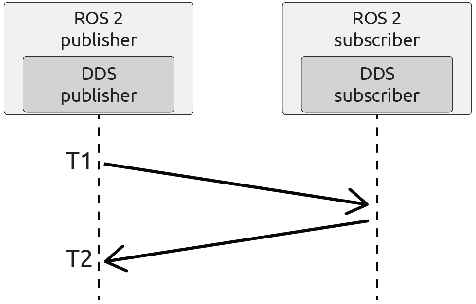
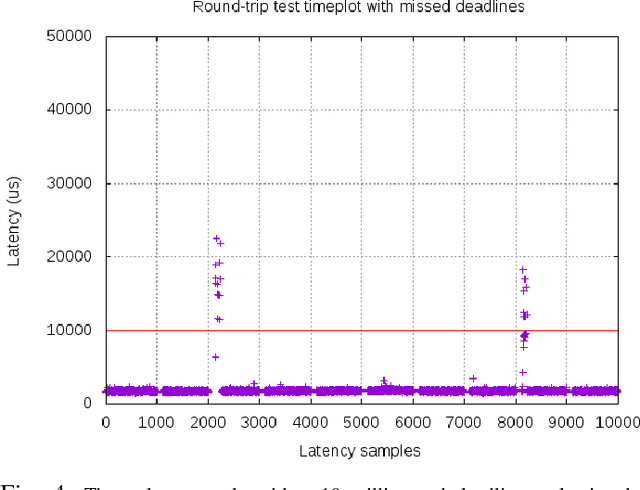
In this work we present an experimental setup to show the suitability of ROS 2.0 for real-time robotic applications. We disclose an evaluation of ROS 2.0 communications in a robotic inter-component (hardware) communication case on top of Linux. We benchmark and study the worst case latencies and missed deadlines to characterize ROS 2.0 communications for real-time applications. We demonstrate experimentally how computation and network congestion impacts the communication latencies and ultimately, propose a setup that, under certain conditions, mitigates these delays and obtains bounded traffic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge