Toward Wheeled Mobility on Vertically Challenging Terrain: Platforms, Datasets, and Algorithms
Paper and Code
Mar 02, 2023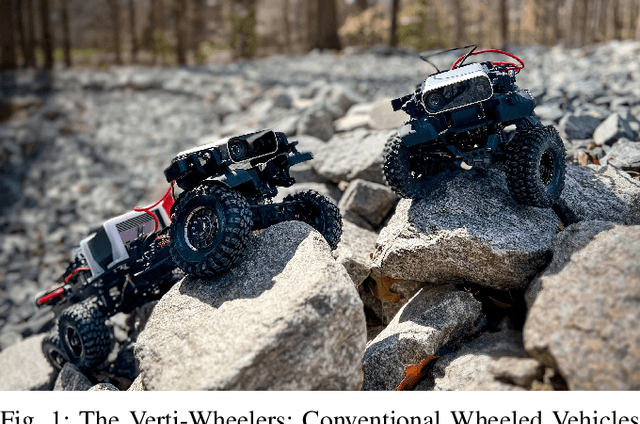
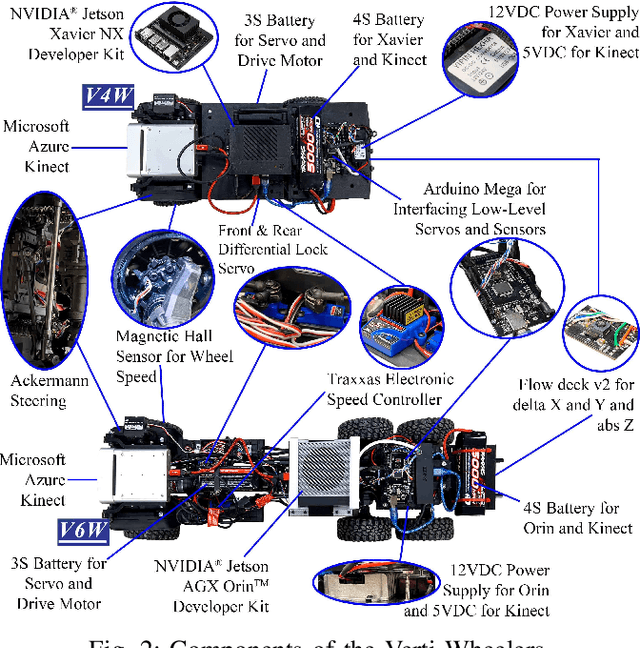
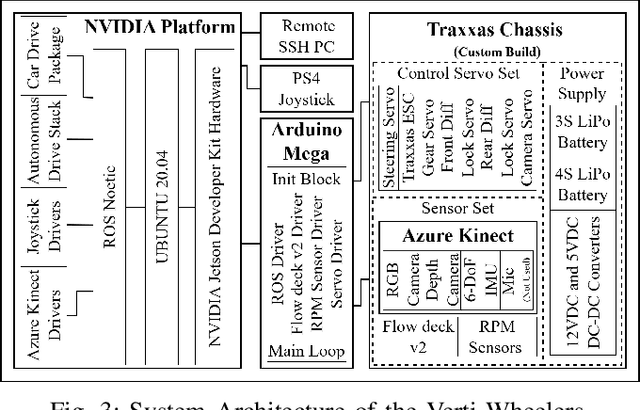
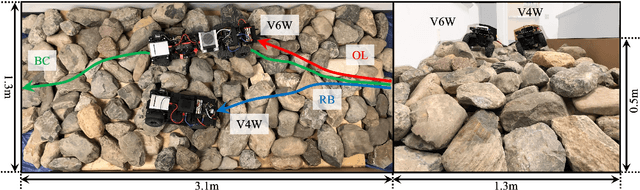
Most conventional wheeled robots can only move in flat environments and simply divide their planar workspaces into free spaces and obstacles. Deeming obstacles as non-traversable significantly limits wheeled robots' mobility in real-world, non-flat, off-road environments, where part of the terrain (e.g., steep slopes, rugged boulders) will be treated as non-traversable obstacles. To improve wheeled mobility in those non-flat environments with vertically challenging terrain, we present two wheeled platforms with little hardware modification compared to conventional wheeled robots; we collect datasets of our wheeled robots crawling over previously non-traversable, vertically challenging terrain to facilitate data-driven mobility; we also present algorithms and their experimental results to show that conventional wheeled robots have previously unrealized potential of moving through vertically challenging terrain. We make our platforms, datasets, and algorithms publicly available to facilitate future research on wheeled mobility.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge