The Unreasonable Effectiveness of the Final Batch Normalization Layer
Paper and Code
Sep 18, 2021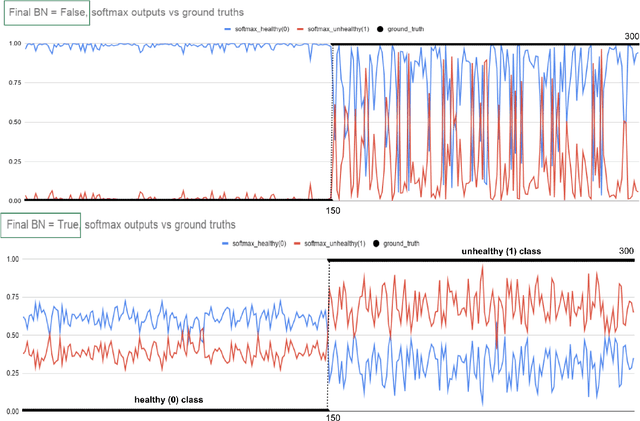

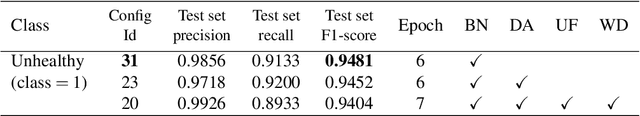
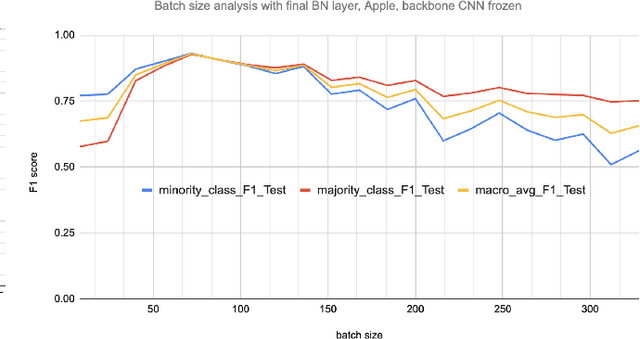
Early-stage disease indications are rarely recorded in real-world domains, such as Agriculture and Healthcare, and yet, their accurate identification is critical in that point of time. In this type of highly imbalanced classification problems, which encompass complex features, deep learning (DL) is much needed because of its strong detection capabilities. At the same time, DL is observed in practice to favor majority over minority classes and consequently suffer from inaccurate detection of the targeted early-stage indications. In this work, we extend the study done by Kocaman et al., 2020, showing that the final BN layer, when placed before the softmax output layer, has a considerable impact in highly imbalanced image classification problems as well as undermines the role of the softmax outputs as an uncertainty measure. This current study addresses additional hypotheses and reports on the following findings: (i) the performance gain after adding the final BN layer in highly imbalanced settings could still be achieved after removing this additional BN layer in inference; (ii) there is a certain threshold for the imbalance ratio upon which the progress gained by the final BN layer reaches its peak; (iii) the batch size also plays a role and affects the outcome of the final BN application; (iv) the impact of the BN application is also reproducible on other datasets and when utilizing much simpler neural architectures; (v) the reported BN effect occurs only per a single majority class and multiple minority classes i.e., no improvements are evident when there are two majority classes; and finally, (vi) utilizing this BN layer with sigmoid activation has almost no impact when dealing with a strongly imbalanced image classification tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge