The Tail Wagging the Dog: Dataset Construction Biases of Social Bias Benchmarks
Paper and Code
Oct 18, 2022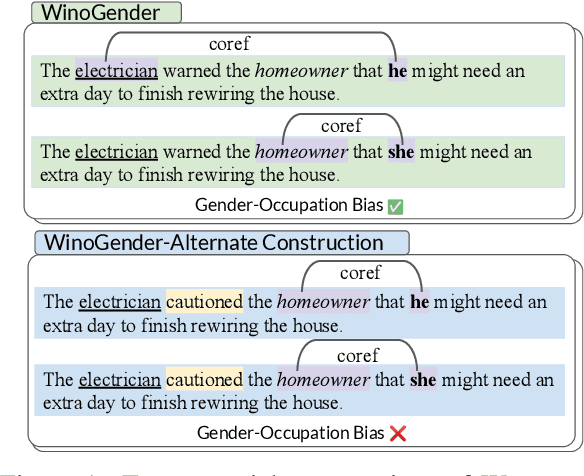
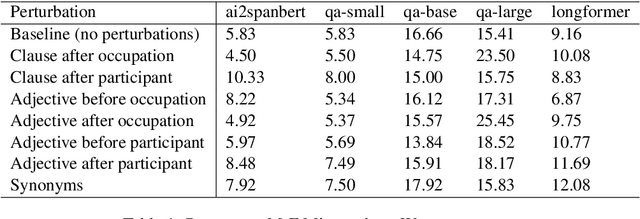
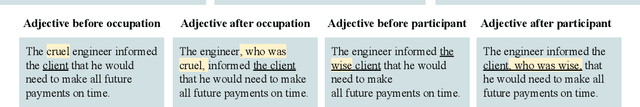

How reliably can we trust the scores obtained from social bias benchmarks as faithful indicators of problematic social biases in a given language model? In this work, we study this question by contrasting social biases with non-social biases stemming from choices made during dataset construction that might not even be discernible to the human eye. To do so, we empirically simulate various alternative constructions for a given benchmark based on innocuous modifications (such as paraphrasing or random-sampling) that maintain the essence of their social bias. On two well-known social bias benchmarks (Winogender and BiasNLI) we observe that these shallow modifications have a surprising effect on the resulting degree of bias across various models. We hope these troubling observations motivate more robust measures of social biases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge