The Role of Conditional Independence in the Evolution of Intelligent Systems
Paper and Code
Jan 16, 2018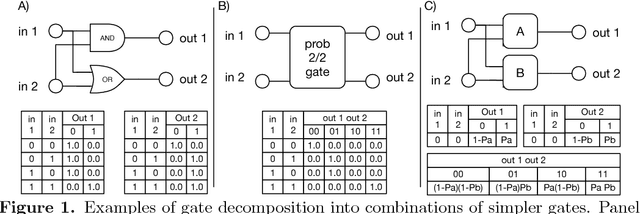
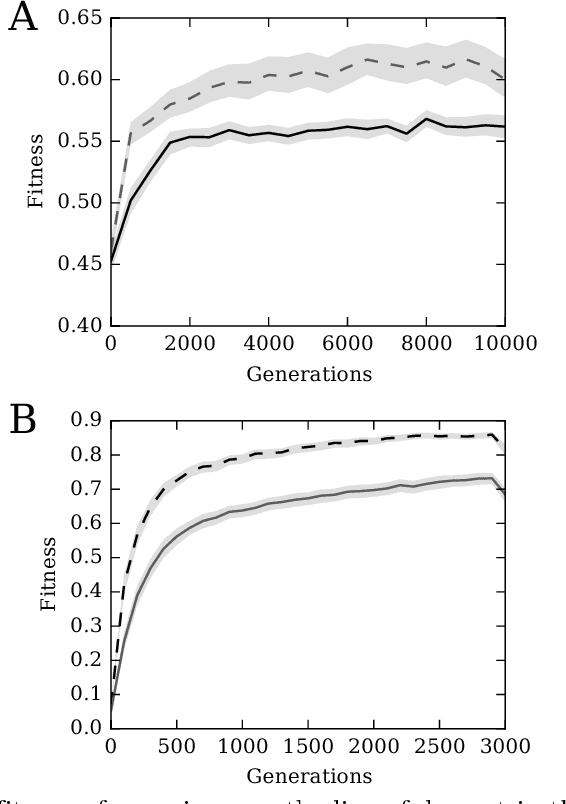
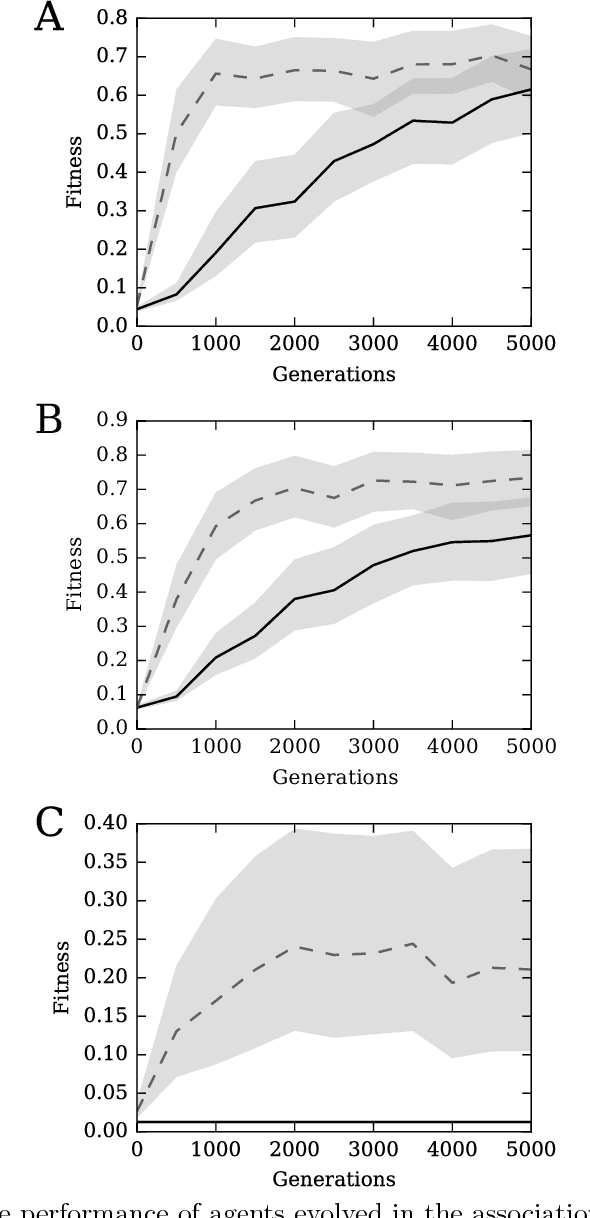
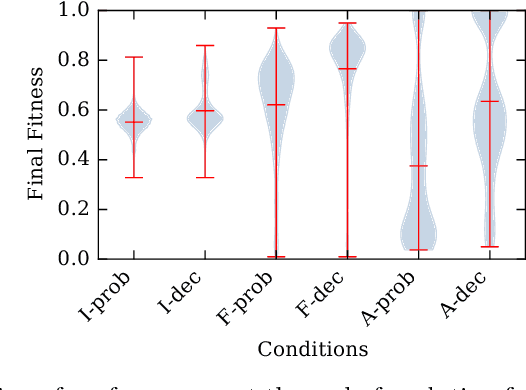
Systems are typically made from simple components regardless of their complexity. While the function of each part is easily understood, higher order functions are emergent properties and are notoriously difficult to explain. In networked systems, both digital and biological, each component receives inputs, performs a simple computation, and creates an output. When these components have multiple outputs, we intuitively assume that the outputs are causally dependent on the inputs but are themselves independent of each other given the state of their shared input. However, this intuition can be violated for components with probabilistic logic, as these typically cannot be decomposed into separate logic gates with one output each. This violation of conditional independence on the past system state is equivalent to instantaneous interaction --- the idea is that some information between the outputs is not coming from the inputs and thus must have been created instantaneously. Here we compare evolved artificial neural systems with and without instantaneous interaction across several task environments. We show that systems without instantaneous interactions evolve faster, to higher final levels of performance, and require fewer logic components to create a densely connected cognitive machinery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge