The IBM 2016 English Conversational Telephone Speech Recognition System
Paper and Code
Jun 22, 2016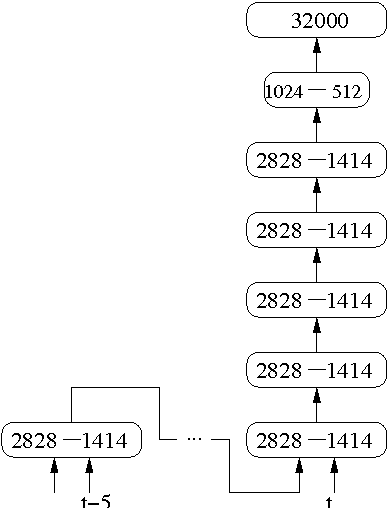
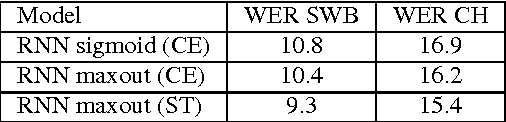
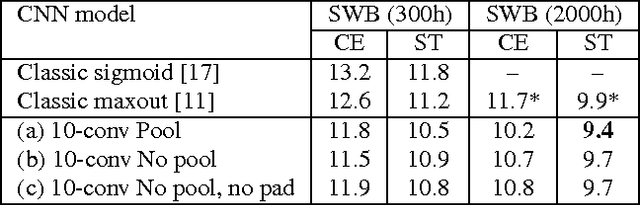
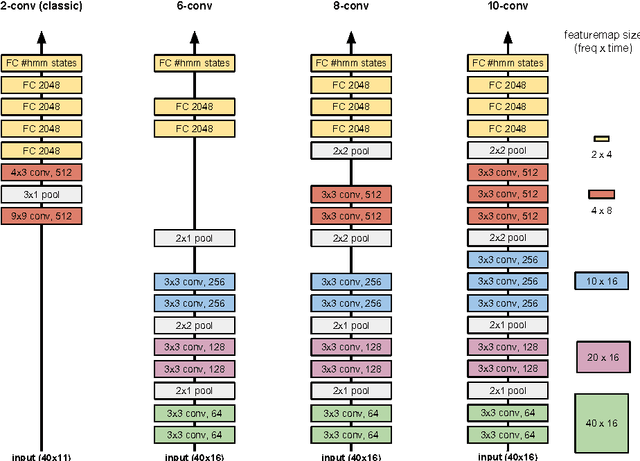
We describe a collection of acoustic and language modeling techniques that lowered the word error rate of our English conversational telephone LVCSR system to a record 6.6% on the Switchboard subset of the Hub5 2000 evaluation testset. On the acoustic side, we use a score fusion of three strong models: recurrent nets with maxout activations, very deep convolutional nets with 3x3 kernels, and bidirectional long short-term memory nets which operate on FMLLR and i-vector features. On the language modeling side, we use an updated model "M" and hierarchical neural network LMs.
* Submitted to Interspeech 2016
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge