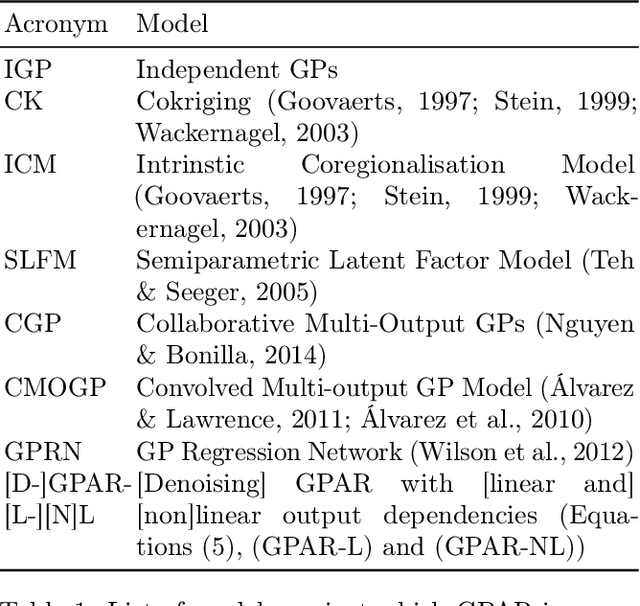
The Gaussian Process Autoregressive Regression Model (GPAR)
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2018

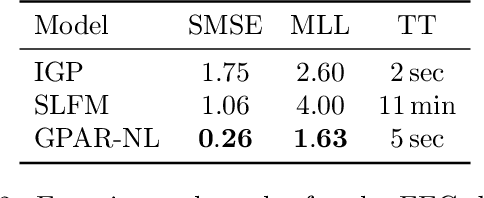
Multi-output regression models must exploit dependencies between outputs to maximise predictive performance. The application of Gaussian processes (GPs) to this setting typically yields models that are computationally demanding and have limited representational power. We present the Gaussian Process Autoregressive Regression (GPAR) model, a scalable multi-output GP model that is able to capture nonlinear, possibly input-varying, dependencies between outputs in a simple and tractable way: the product rule is used to decompose the joint distribution over the outputs into a set of conditionals, each of which is modelled by a standard GP. GPAR's efficacy is demonstrated on a variety of synthetic and real-world problems, outperforming existing GP models and achieving state-of-the-art performance on the tasks with existing benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge