Temporal Subspace Clustering for Molecular Dynamics Data
Paper and Code
Jul 31, 2024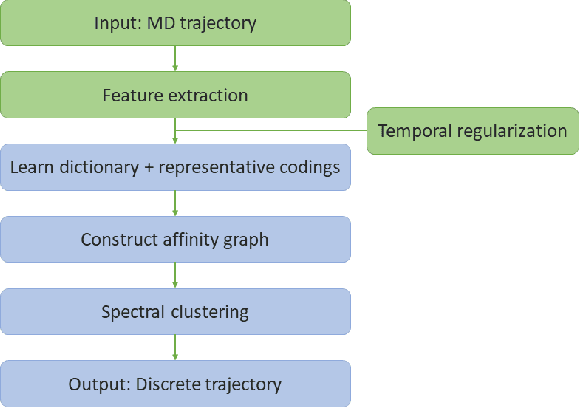
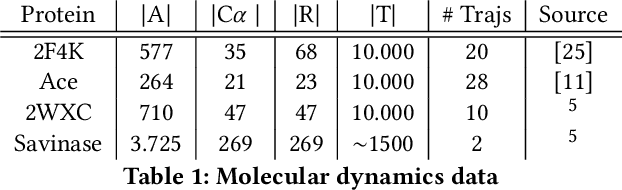
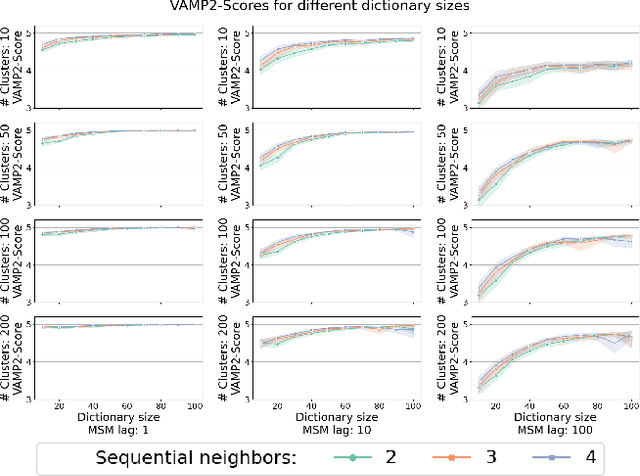
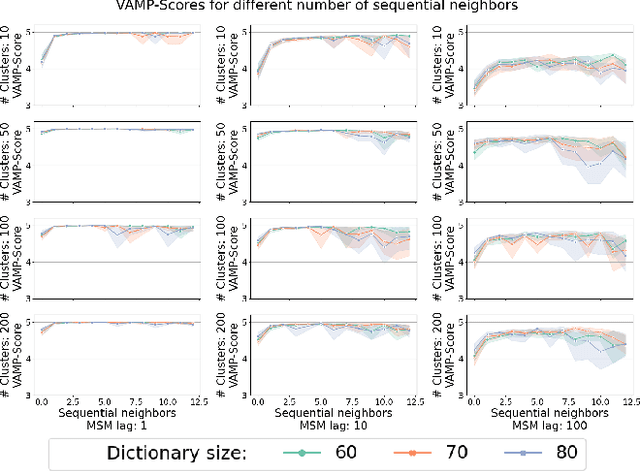
We introduce MOSCITO (MOlecular Dynamics Subspace Clustering with Temporal Observance), a subspace clustering for molecular dynamics data. MOSCITO groups those timesteps of a molecular dynamics trajectory together into clusters in which the molecule has similar conformations. In contrast to state-of-the-art methods, MOSCITO takes advantage of sequential relationships found in time series data. Unlike existing work, MOSCITO does not need a two-step procedure with tedious post-processing, but directly models essential properties of the data. Interpreting clusters as Markov states allows us to evaluate the clustering performance based on the resulting Markov state models. In experiments on 60 trajectories and 4 different proteins, we show that the performance of MOSCITO achieves state-of-the-art performance in a novel single-step method. Moreover, by modeling temporal aspects, MOSCITO obtains better segmentation of trajectories, especially for small numbers of clusters.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge