Synthetic Dataset Generation for Privacy-Preserving Machine Learning
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2022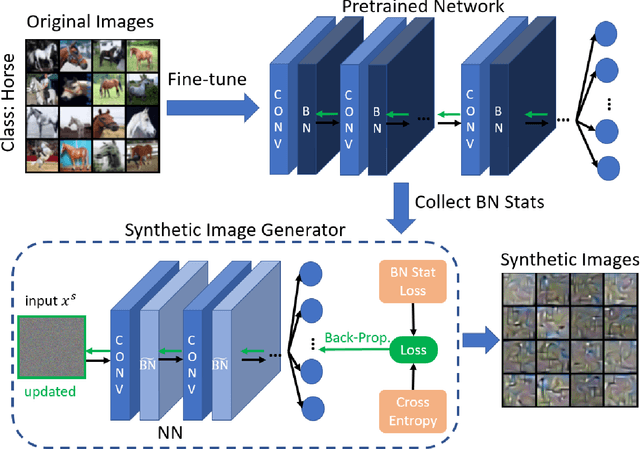
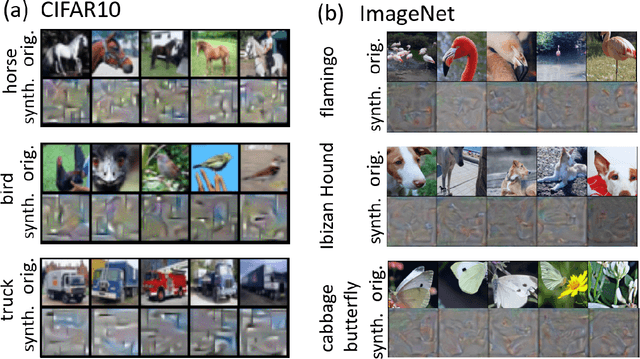
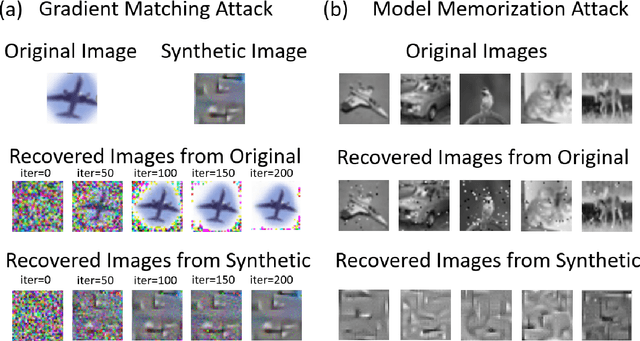
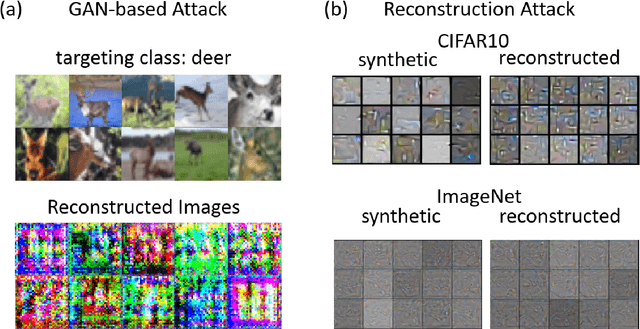
Machine Learning (ML) has achieved enormous success in solving a variety of problems in computer vision, speech recognition, object detection, to name a few. The principal reason for this success is the availability of huge datasets for training deep neural networks (DNNs). However, datasets cannot be publicly released if they contain sensitive information such as medical records, and data privacy becomes a major concern. Encryption methods could be a possible solution, however their deployment on ML applications seriously impacts classification accuracy and results in substantial computational overhead. Alternatively, obfuscation techniques could be used, but maintaining a good trade-off between visual privacy and accuracy is challenging. In this paper, we propose a method to generate secure synthetic datasets from the original private datasets. Given a network with Batch Normalization (BN) layers pretrained on the original dataset, we first record the class-wise BN layer statistics. Next, we generate the synthetic dataset by optimizing random noise such that the synthetic data match the layer-wise statistical distribution of original images. We evaluate our method on image classification datasets (CIFAR10, ImageNet) and show that synthetic data can be used in place of the original CIFAR10/ImageNet data for training networks from scratch, producing comparable classification performance. Further, to analyze visual privacy provided by our method, we use Image Quality Metrics and show high degree of visual dissimilarity between the original and synthetic images. Moreover, we show that our proposed method preserves data-privacy under various privacy-leakage attacks including Gradient Matching Attack, Model Memorization Attack, and GAN-based Attack.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge