Suspiciousness of Adversarial Texts to Human
Paper and Code
Oct 06, 2024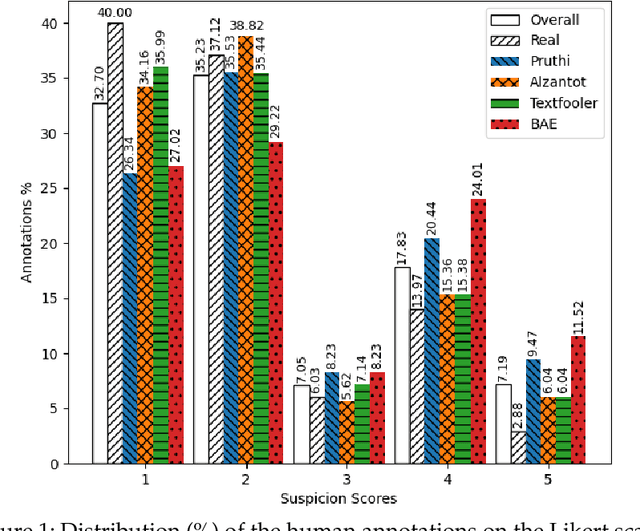


Adversarial examples pose a significant challenge to deep neural networks (DNNs) across both image and text domains, with the intent to degrade model performance through meticulously altered inputs. Adversarial texts, however, are distinct from adversarial images due to their requirement for semantic similarity and the discrete nature of the textual contents. This study delves into the concept of human suspiciousness, a quality distinct from the traditional focus on imperceptibility found in image-based adversarial examples. Unlike images, where adversarial changes are meant to be indistinguishable to the human eye, textual adversarial content must often remain undetected or non-suspicious to human readers, even when the text's purpose is to deceive NLP systems or bypass filters. In this research, we expand the study of human suspiciousness by analyzing how individuals perceive adversarial texts. We gather and publish a novel dataset of Likert-scale human evaluations on the suspiciousness of adversarial sentences, crafted by four widely used adversarial attack methods and assess their correlation with the human ability to detect machine-generated alterations. Additionally, we develop a regression-based model to quantify suspiciousness and establish a baseline for future research in reducing the suspiciousness in adversarial text generation. We also demonstrate how the regressor-generated suspicious scores can be incorporated into adversarial generation methods to produce texts that are less likely to be perceived as computer-generated. We make our human suspiciousness annotated data and our code available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge