Supersonic: Learning to Generate Source Code Optimizations in C/C++
Paper and Code
Oct 02, 2023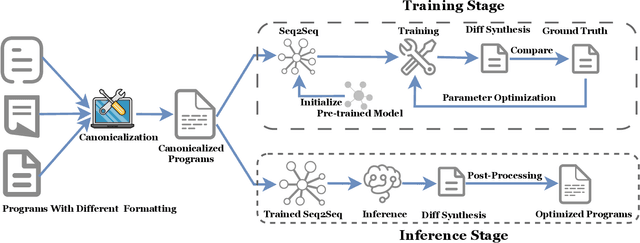

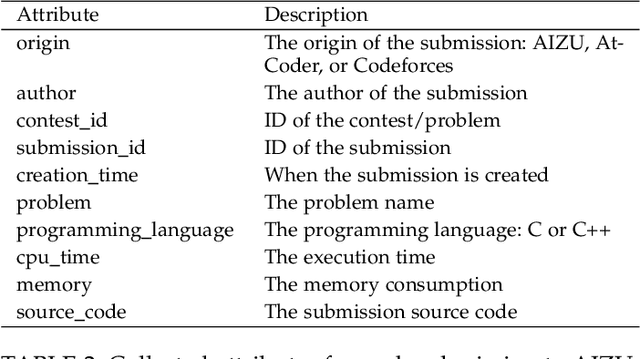
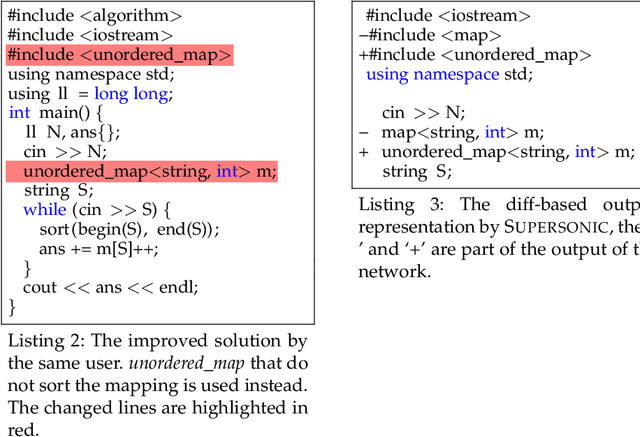
Software optimization refines programs for resource efficiency while preserving functionality. Traditionally, it is a process done by developers and compilers. This paper introduces a third option, automated optimization at the source code level. We present Supersonic, a neural approach targeting minor source code modifications for optimization. Using a seq2seq model, Supersonic is trained on C/C++ program pairs ($x_{t}$, $x_{t+1}$), where $x_{t+1}$ is an optimized version of $x_{t}$, and outputs a diff. Supersonic's performance is benchmarked against OpenAI's GPT-3.5-Turbo and GPT-4 on competitive programming tasks. The experiments show that Supersonic not only outperforms both models on the code optimization task but also minimizes the extent of the change with a model more than 600x smaller than GPT-3.5-Turbo and 3700x smaller than GPT-4.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge