StylePrompter: Enhancing Domain Generalization with Test-Time Style Priors
Paper and Code
Aug 17, 2024
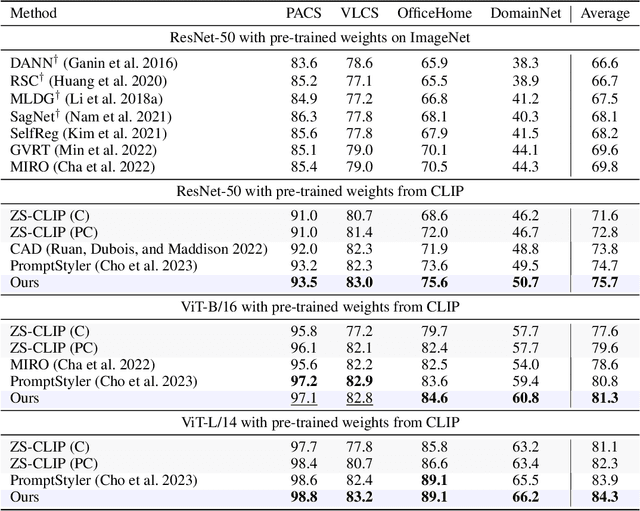

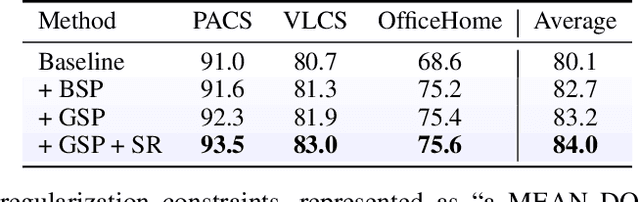
In real-world applications, the sample distribution at the inference stage often differs from the one at the training stage, causing performance degradation of trained deep models. The research on domain generalization (DG) aims to develop robust algorithms that can improve the generalized performance in unseen domains by training on a few domains. However, the domain-agnostic vision model, trained on a limited number of domains using traditional domain generalization methods, cannot guarantee its effectiveness in dealing with unseen domains. The introduction of language can break the closed cognition space of the vision model, providing additional semantic information that cannot be inferred from vision-only datasets. In this paper, we propose to overcome the challenge in previous DG methods by introducing the style prompt in the language modality to adapt the trained model dynamically. In particular, we train a style prompter to extract style information of the current image into an embedding in the token embedding space and place it in front of the candidate category words as prior knowledge to prompt the model. Our open space partition of the style token embedding space and the hand-crafted style regularization enable the trained style prompter to handle data from unknown domains effectively. Extensive experiments verify the effectiveness of our method and demonstrate state-of-the-art performances on multiple public datasets. Codes will be available after the acceptance of this paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge