Streaming Probabilistic PCA for Missing Data with Heteroscedastic Noise
Paper and Code
Oct 10, 2023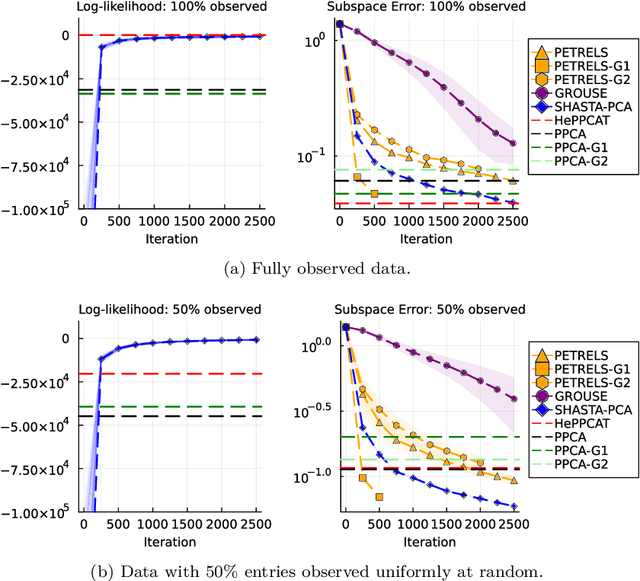
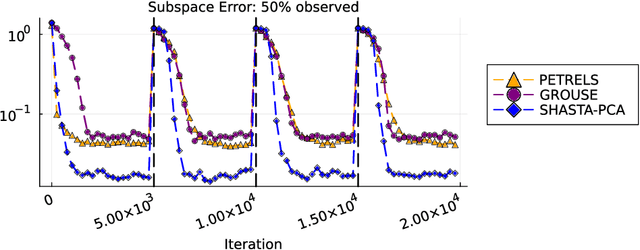
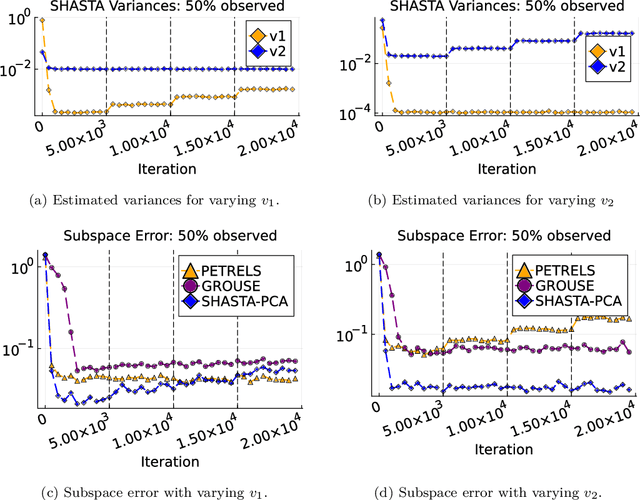
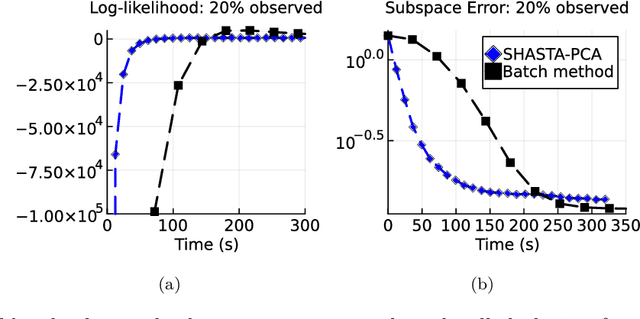
Streaming principal component analysis (PCA) is an integral tool in large-scale machine learning for rapidly estimating low-dimensional subspaces of very high dimensional and high arrival-rate data with missing entries and corrupting noise. However, modern trends increasingly combine data from a variety of sources, meaning they may exhibit heterogeneous quality across samples. Since standard streaming PCA algorithms do not account for non-uniform noise, their subspace estimates can quickly degrade. On the other hand, the recently proposed Heteroscedastic Probabilistic PCA Technique (HePPCAT) addresses this heterogeneity, but it was not designed to handle missing entries and streaming data, nor does it adapt to non-stationary behavior in time series data. This paper proposes the Streaming HeteroscedASTic Algorithm for PCA (SHASTA-PCA) to bridge this divide. SHASTA-PCA employs a stochastic alternating expectation maximization approach that jointly learns the low-rank latent factors and the unknown noise variances from streaming data that may have missing entries and heteroscedastic noise, all while maintaining a low memory and computational footprint. Numerical experiments validate the superior subspace estimation of our method compared to state-of-the-art streaming PCA algorithms in the heteroscedastic setting. Finally, we illustrate SHASTA-PCA applied to highly-heterogeneous real data from astronomy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge