StoryER: Automatic Story Evaluation via Ranking, Rating and Reasoning
Paper and Code
Oct 16, 2022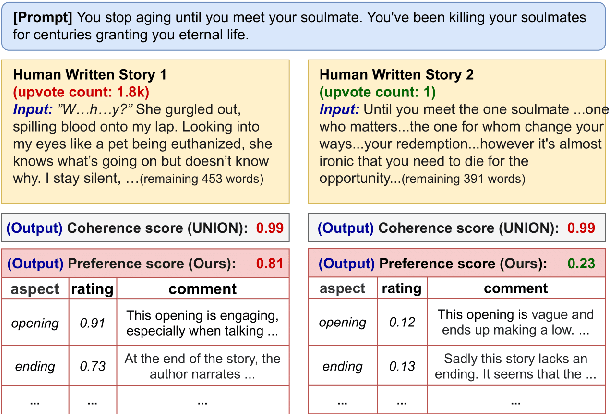
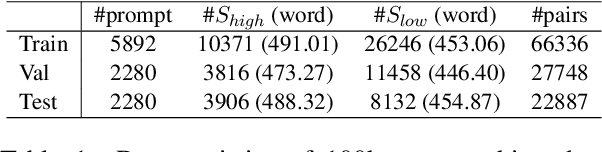
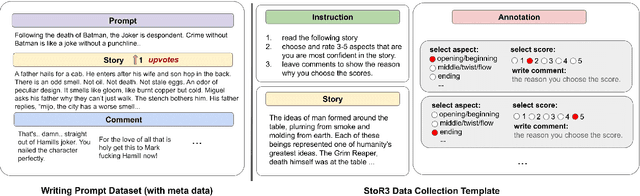
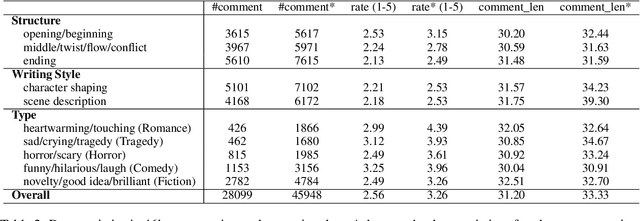
Existing automatic story evaluation methods place a premium on story lexical level coherence, deviating from human preference. We go beyond this limitation by considering a novel \textbf{Story} \textbf{E}valuation method that mimics human preference when judging a story, namely \textbf{StoryER}, which consists of three sub-tasks: \textbf{R}anking, \textbf{R}ating and \textbf{R}easoning. Given either a machine-generated or a human-written story, StoryER requires the machine to output 1) a preference score that corresponds to human preference, 2) specific ratings and their corresponding confidences and 3) comments for various aspects (e.g., opening, character-shaping). To support these tasks, we introduce a well-annotated dataset comprising (i) 100k ranked story pairs; and (ii) a set of 46k ratings and comments on various aspects of the story. We finetune Longformer-Encoder-Decoder (LED) on the collected dataset, with the encoder responsible for preference score and aspect prediction and the decoder for comment generation. Our comprehensive experiments result in a competitive benchmark for each task, showing the high correlation to human preference. In addition, we have witnessed the joint learning of the preference scores, the aspect ratings, and the comments brings gain in each single task. Our dataset and benchmarks are publicly available to advance the research of story evaluation tasks.\footnote{Dataset and pre-trained model demo are available at anonymous website \url{http://storytelling-lab.com/eval} and \url{https://github.com/sairin1202/StoryER}}
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge