Stochastic Games for Interactive Manipulation Domains
Paper and Code
Mar 07, 2024
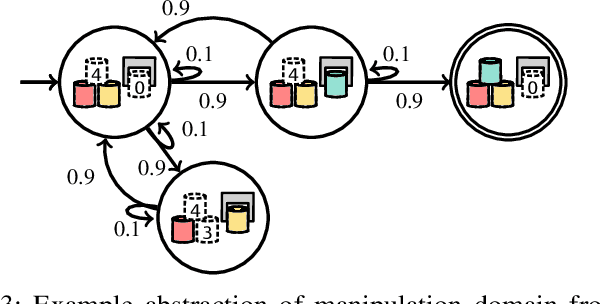
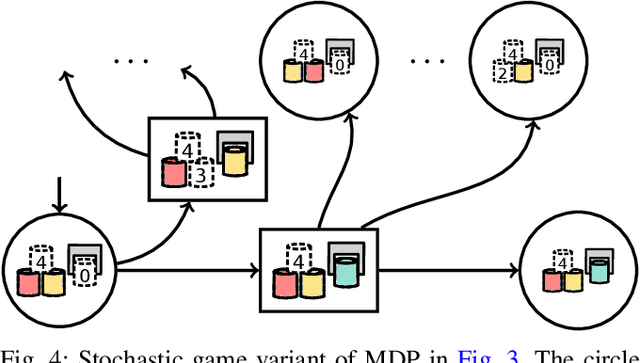
As robots become more prevalent, the complexity of robot-robot, robot-human, and robot-environment interactions increases. In these interactions, a robot needs to consider not only the effects of its own actions, but also the effects of other agents' actions and the possible interactions between agents. Previous works have considered reactive synthesis, where the human/environment is modeled as a deterministic, adversarial agent; as well as probabilistic synthesis, where the human/environment is modeled via a Markov chain. While they provide strong theoretical frameworks, there are still many aspects of human-robot interaction that cannot be fully expressed and many assumptions that must be made in each model. In this work, we propose stochastic games as a general model for human-robot interaction, which subsumes the expressivity of all previous representations. In addition, it allows us to make fewer modeling assumptions and leads to more natural and powerful models of interaction. We introduce the semantics of this abstraction and show how existing tools can be utilized to synthesize strategies to achieve complex tasks with guarantees. Further, we discuss the current computational limitations and improve the scalability by two orders of magnitude by a new way of constructing models for PRISM-games.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge