Statistical Consequences of Dueling Bandits
Paper and Code
Oct 16, 2021
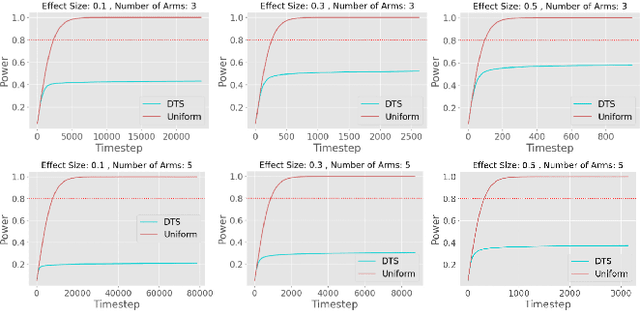
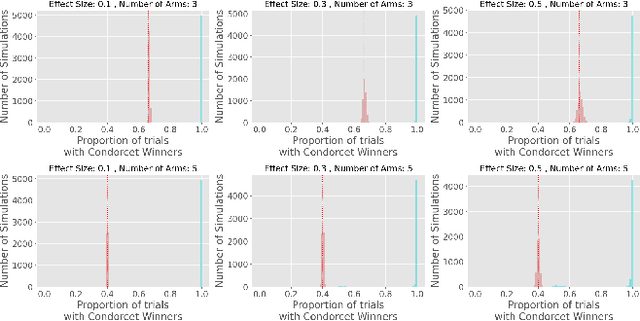
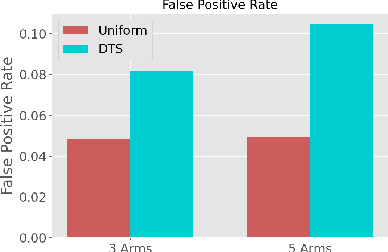
Multi-Armed-Bandit frameworks have often been used by researchers to assess educational interventions, however, recent work has shown that it is more beneficial for a student to provide qualitative feedback through preference elicitation between different alternatives, making a dueling bandits framework more appropriate. In this paper, we explore the statistical quality of data under this framework by comparing traditional uniform sampling to a dueling bandit algorithm and find that dueling bandit algorithms perform well at cumulative regret minimisation, but lead to inflated Type-I error rates and reduced power under certain circumstances. Through these results we provide insight into the challenges and opportunities in using dueling bandit algorithms to run adaptive experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge