Station-to-User Transfer Learning: Towards Explainable User Clustering Through Latent Trip Signatures Using Tidal-Regularized Non-Negative Matrix Factorization
Paper and Code
Apr 27, 2020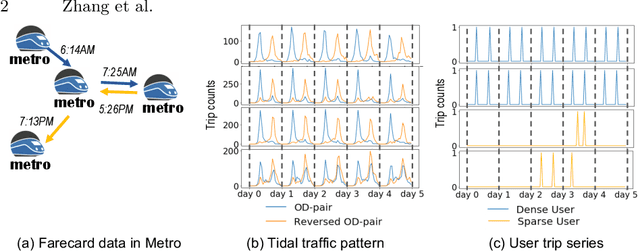
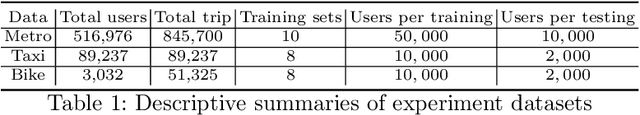
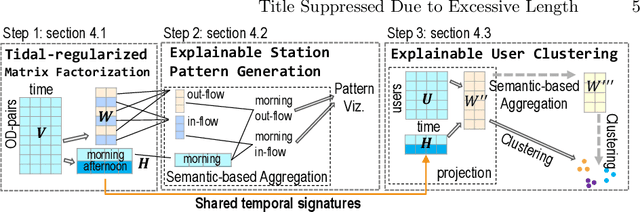
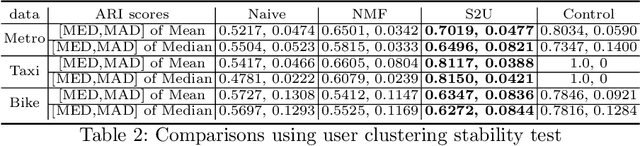
Urban areas provide us with a treasure trove of available data capturing almost every aspect of a population's life. This work focuses on mobility data and how it will help improve our understanding of urban mobility patterns. Readily available and sizable farecard data captures trips in a public transportation network. However, such data typically lacks temporal modalities and as such the task of inferring trip semantic, station function, and user profile is quite challenging. As existing approaches either focus on station-level or user-level signals, they are prone to overfitting and generate less credible and insightful results. To properly learn such characteristics from trip data, we propose a Collective Learning Framework through Latent Representation, which augments user-level learning with collective patterns learned from station-level signals. This framework uses a novel, so-called Tidal-Regularized Non-negative Matrix Factorization method, which incorporates domain knowledge in the form of temporal passenger flow patterns in generic Non-negative Matrix Factorization. To evaluate our model performance, a user stability test based on the classical Rand Index is introduced as a metric to benchmark different unsupervised learning models. We provide a qualitative analysis of the station functions and user profiles for the Washington D.C. metro and show how our method supports spatiotemporal intra-city mobility exploration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge