SQuAT: Sharpness- and Quantization-Aware Training for BERT
Paper and Code
Oct 13, 2022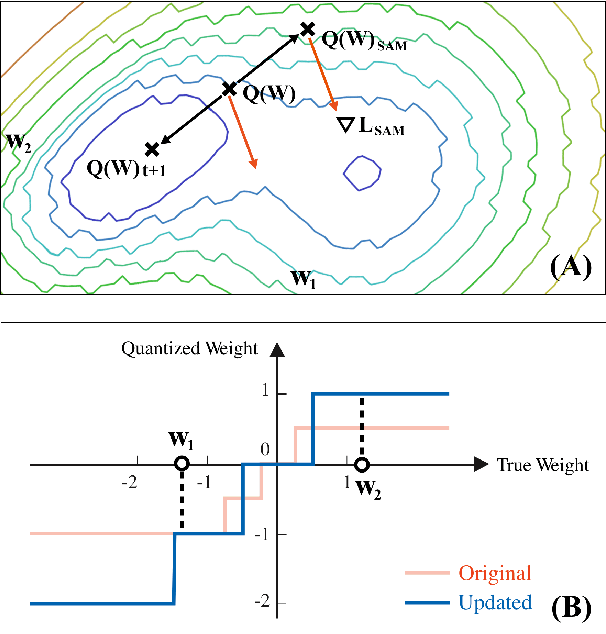
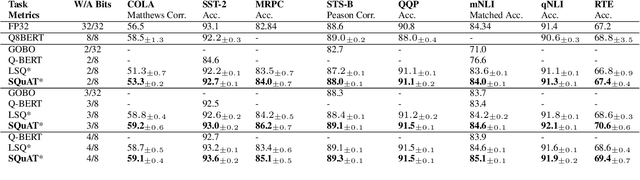
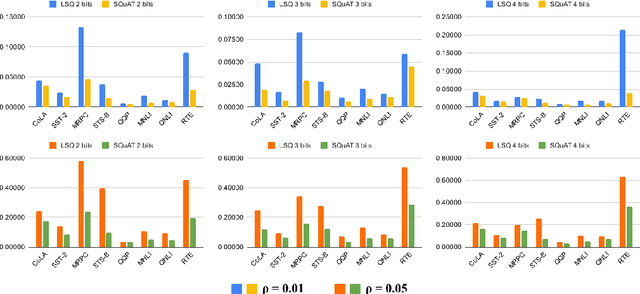
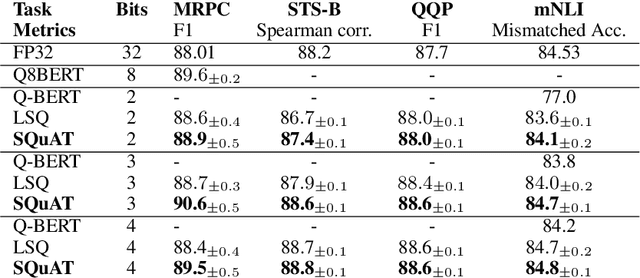
Quantization is an effective technique to reduce memory footprint, inference latency, and power consumption of deep learning models. However, existing quantization methods suffer from accuracy degradation compared to full-precision (FP) models due to the errors introduced by coarse gradient estimation through non-differentiable quantization layers. The existence of sharp local minima in the loss landscapes of overparameterized models (e.g., Transformers) tends to aggravate such performance penalty in low-bit (2, 4 bits) settings. In this work, we propose sharpness- and quantization-aware training (SQuAT), which would encourage the model to converge to flatter minima while performing quantization-aware training. Our proposed method alternates training between sharpness objective and step-size objective, which could potentially let the model learn the most suitable parameter update magnitude to reach convergence near-flat minima. Extensive experiments show that our method can consistently outperform state-of-the-art quantized BERT models under 2, 3, and 4-bit settings on GLUE benchmarks by 1%, and can sometimes even outperform full precision (32-bit) models. Our experiments on empirical measurement of sharpness also suggest that our method would lead to flatter minima compared to other quantization methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge