SplatMAP: Online Dense Monocular SLAM with 3D Gaussian Splatting
Paper and Code
Jan 14, 2025
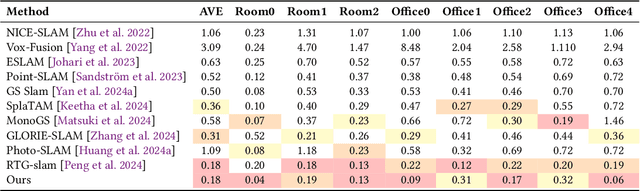

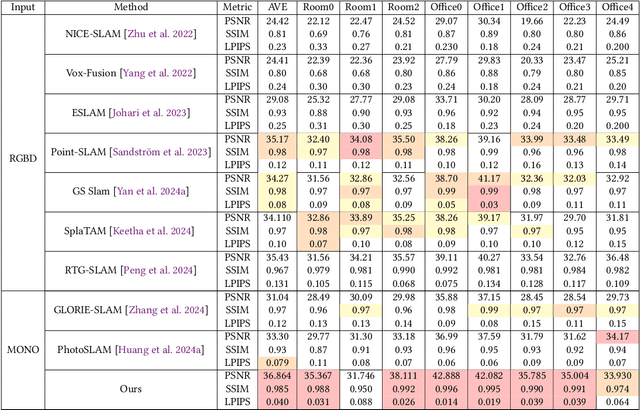
Achieving high-fidelity 3D reconstruction from monocular video remains challenging due to the inherent limitations of traditional methods like Structure-from-Motion (SfM) and monocular SLAM in accurately capturing scene details. While differentiable rendering techniques such as Neural Radiance Fields (NeRF) address some of these challenges, their high computational costs make them unsuitable for real-time applications. Additionally, existing 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) methods often focus on photometric consistency, neglecting geometric accuracy and failing to exploit SLAM's dynamic depth and pose updates for scene refinement. We propose a framework integrating dense SLAM with 3DGS for real-time, high-fidelity dense reconstruction. Our approach introduces SLAM-Informed Adaptive Densification, which dynamically updates and densifies the Gaussian model by leveraging dense point clouds from SLAM. Additionally, we incorporate Geometry-Guided Optimization, which combines edge-aware geometric constraints and photometric consistency to jointly optimize the appearance and geometry of the 3DGS scene representation, enabling detailed and accurate SLAM mapping reconstruction. Experiments on the Replica and TUM-RGBD datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach, achieving state-of-the-art results among monocular systems. Specifically, our method achieves a PSNR of 36.864, SSIM of 0.985, and LPIPS of 0.040 on Replica, representing improvements of 10.7%, 6.4%, and 49.4%, respectively, over the previous SOTA. On TUM-RGBD, our method outperforms the closest baseline by 10.2%, 6.6%, and 34.7% in the same metrics. These results highlight the potential of our framework in bridging the gap between photometric and geometric dense 3D scene representations, paving the way for practical and efficient monocular dense reconstruction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge