Spherical Transformer
Paper and Code
Feb 11, 2022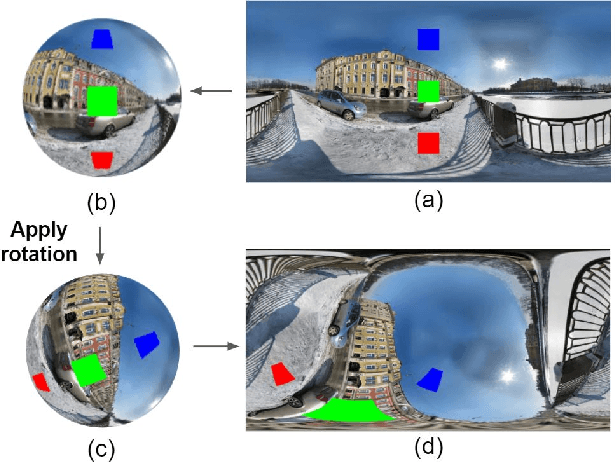
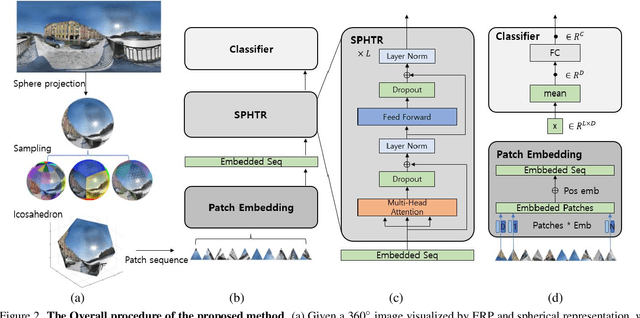
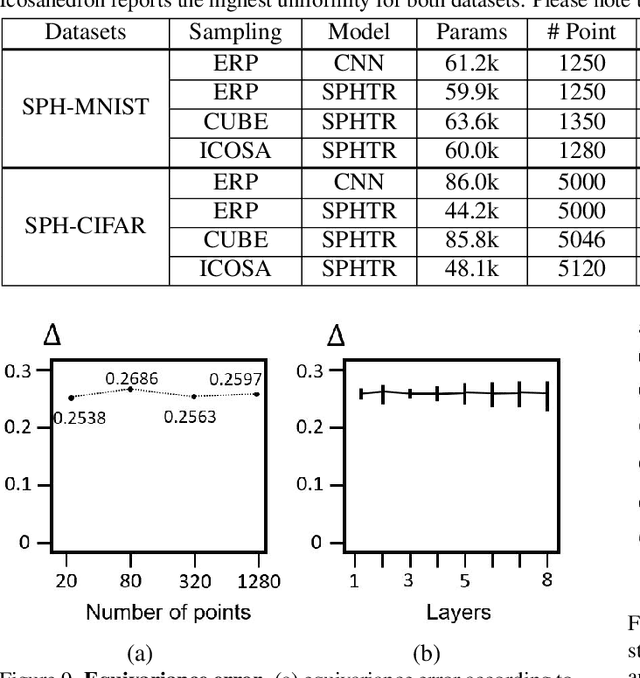
Using convolutional neural networks for 360images can induce sub-optimal performance due to distortions entailed by a planar projection. The distortion gets deteriorated when a rotation is applied to the 360image. Thus, many researches based on convolutions attempt to reduce the distortions to learn accurate representation. In contrast, we leverage the transformer architecture to solve image classification problems for 360images. Using the proposed transformer for 360images has two advantages. First, our method does not require the erroneous planar projection process by sampling pixels from the sphere surface. Second, our sampling method based on regular polyhedrons makes low rotation equivariance errors, because specific rotations can be reduced to permutations of faces. In experiments, we validate our network on two aspects, as follows. First, we show that using a transformer with highly uniform sampling methods can help reduce the distortion. Second, we demonstrate that the transformer architecture can achieve rotation equivariance on specific rotations. We compare our method to other state-of-the-art algorithms using the SPH-MNIST, SPH-CIFAR, and SUN360 datasets and show that our method is competitive with other methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge