SPF-CellTracker: Tracking multiple cells with strongly-correlated moves using a spatial particle filter
Paper and Code
May 27, 2016
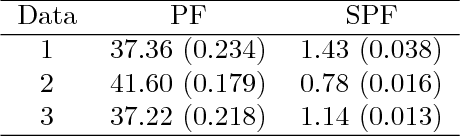
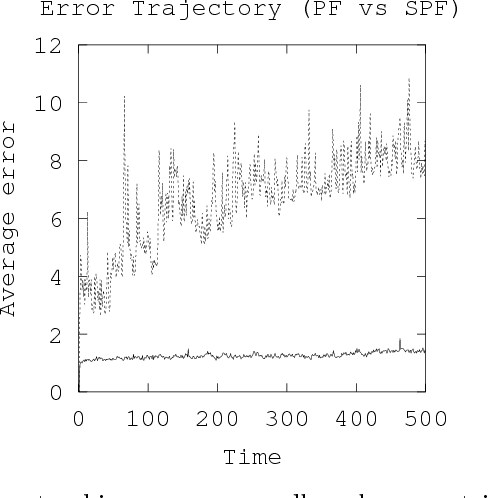
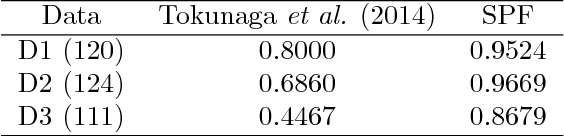
Tracking many cells in time-lapse 3D image sequences is an important challenging task of bioimage informatics. Motivated by a study of brain-wide 4D imaging of neural activity in C. elegans, we present a new method of multi-cell tracking. Data types to which the method is applicable are characterized as follows: (i) cells are imaged as globular-like objects, (ii) it is difficult to distinguish cells based only on shape and size, (iii) the number of imaged cells ranges in several hundreds, (iv) moves of nearly-located cells are strongly correlated and (v) cells do not divide. We developed a tracking software suite which we call SPF-CellTracker. Incorporating dependency on cells' moves into prediction model is the key to reduce the tracking errors: cell-switching and coalescence of tracked positions. We model target cells' correlated moves as a Markov random field and we also derive a fast computation algorithm, which we call spatial particle filter. With the live-imaging data of nuclei of C. elegans neurons in which approximately 120 nuclei of neurons are imaged, we demonstrate an advantage of the proposed method over the standard particle filter and a method developed by Tokunaga et al. (2014).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge