SPEED+: Next Generation Dataset for Spacecraft Pose Estimation across Domain Gap
Paper and Code
Oct 06, 2021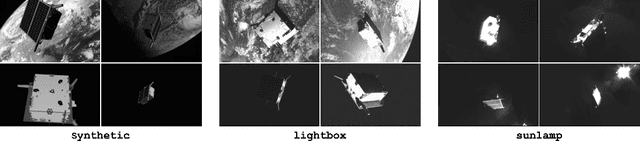
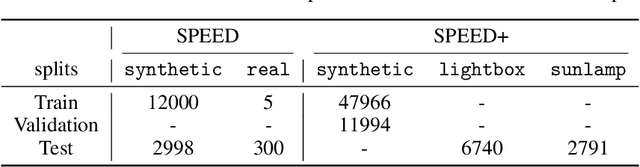

Autonomous vision-based spaceborne navigation is an enabling technology for future on-orbit servicing and space logistics missions. While computer vision in general has benefited from Machine Learning (ML), training and validating spaceborne ML models are extremely challenging due to the impracticality of acquiring a large-scale labeled dataset of images of the intended target in the space environment. Existing datasets, such as Spacecraft PosE Estimation Dataset (SPEED), have so far mostly relied on synthetic images for both training and validation, which are easy to mass-produce but fail to resemble the visual features and illumination variability inherent to the target spaceborne images. In order to bridge the gap between the current practices and the intended applications in future space missions, this paper introduces SPEED+: the next generation spacecraft pose estimation dataset with specific emphasis on domain gap. In addition to 60,000 synthetic images for training, SPEED+ includes 9,531 simulated images of a spacecraft mockup model captured from the Testbed for Rendezvous and Optical Navigation (TRON) facility. TRON is a first-of-a-kind robotic testbed capable of capturing an arbitrary number of target images with accurate and maximally diverse pose labels and high-fidelity spaceborne illumination conditions. SPEED+ will be used in the upcoming international Satellite Pose Estimation Challenge co-hosted with the Advanced Concepts Team of the European Space Agency to evaluate and compare the robustness of spaceborne ML models trained on synthetic images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge