Spectrum-inspired Low-light Image Translation for Saliency Detection
Paper and Code
Mar 17, 2023

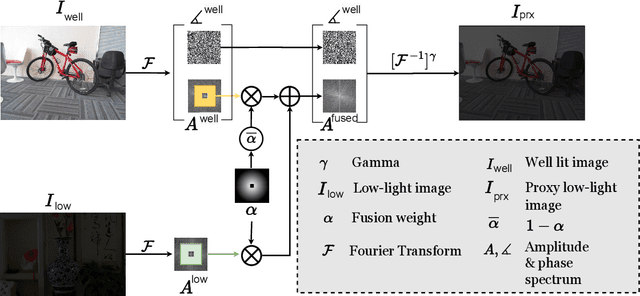

Saliency detection methods are central to several real-world applications such as robot navigation and satellite imagery. However, the performance of existing methods deteriorate under low-light conditions because training datasets mostly comprise of well-lit images. One possible solution is to collect a new dataset for low-light conditions. This involves pixel-level annotations, which is not only tedious and time-consuming but also infeasible if a huge training corpus is required. We propose a technique that performs classical band-pass filtering in the Fourier space to transform well-lit images to low-light images and use them as a proxy for real low-light images. Unlike popular deep learning approaches which require learning thousands of parameters and enormous amounts of training data, the proposed transformation is fast and simple and easy to extend to other tasks such as low-light depth estimation. Our experiments show that the state-of-the-art saliency detection and depth estimation networks trained on our proxy low-light images perform significantly better on real low-light images than networks trained using existing strategies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge