Sparsity through evolutionary pruning prevents neuronal networks from overfitting
Paper and Code
Nov 07, 2019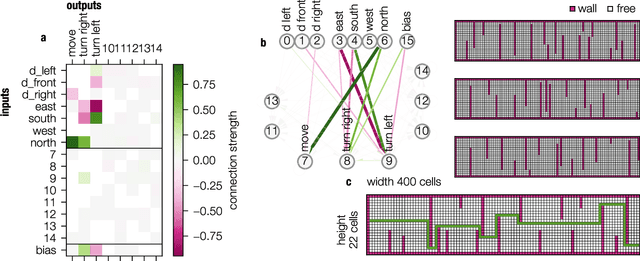
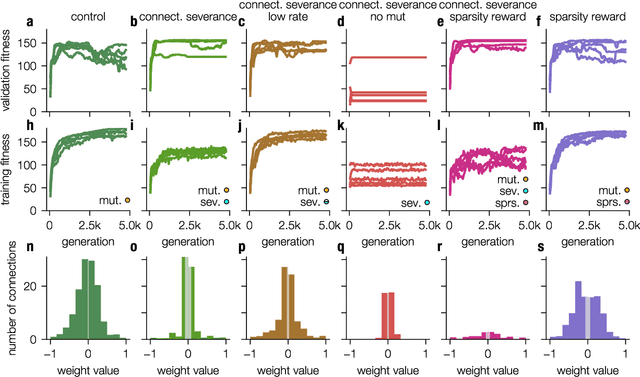
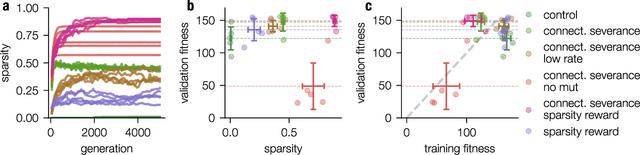
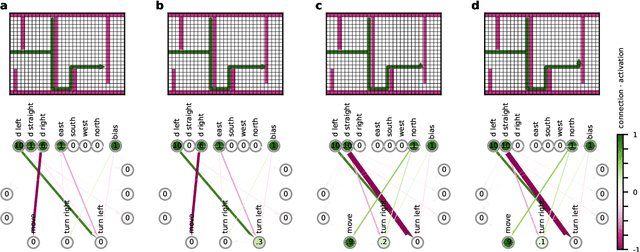
Modern Machine learning techniques take advantage of the exponentially rising calculation power in new generation processor units. Thus, the number of parameters which are trained to resolve complex tasks was highly increased over the last decades. However, still the networks fail - in contrast to our brain - to develop general intelligence in the sense of being able to solve several complex tasks with only one network architecture. This could be the case because the brain is not a randomly initialized neural network, which has to be trained by simply investing a lot of calculation power, but has from birth some fixed hierarchical structure. To make progress in decoding the structural basis of biological neural networks we here chose a bottom-up approach, where we evolutionarily trained small neural networks in performing a maze task. This simple maze task requires dynamical decision making with delayed rewards. We were able to show that during the evolutionary optimization random severance of connections lead to better generalization performance of the networks compared to fully connected networks. We conclude that sparsity is a central property of neural networks and should be considered for modern Machine learning approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge