Sparse convolutional context-aware multiple instance learning for whole slide image classification
Paper and Code
May 06, 2021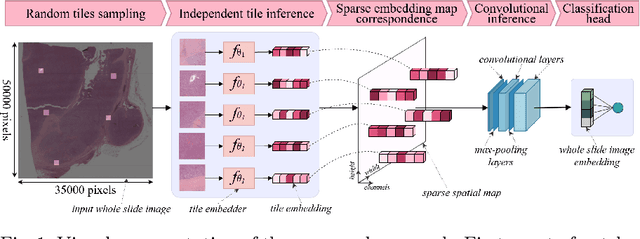
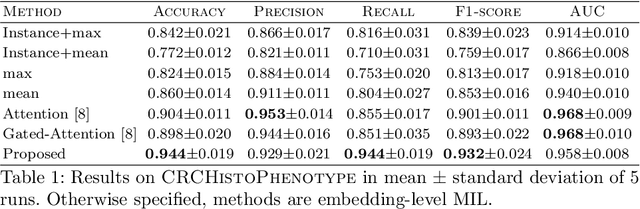
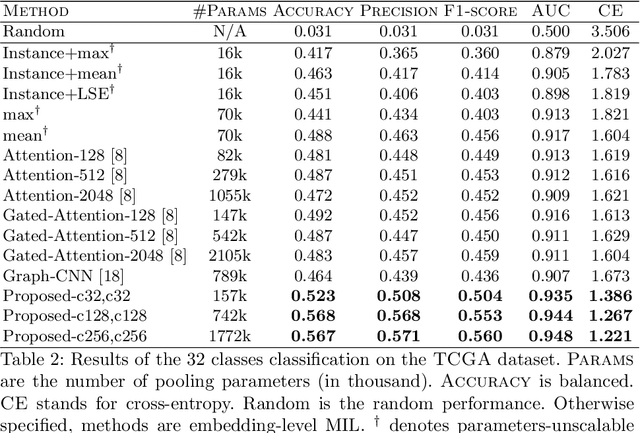
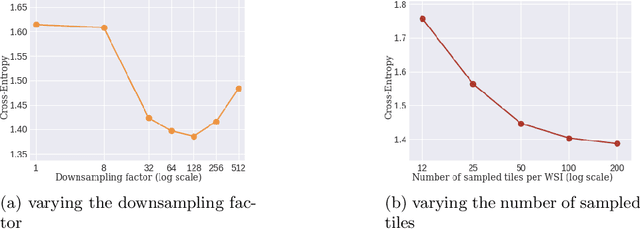
Whole slide microscopic slides display many cues about the underlying tissue guiding diagnostic and the choice of therapy for many diseases. However, their enormous size often in gigapixels hampers the use of traditional neural network architectures. To tackle this issue, multiple instance learning (MIL) classifies bags of patches instead of whole slide images. Most MIL strategies consider that patches are independent and identically distributed. Our approach presents a paradigm shift through the integration of spatial information of patches with a sparse-input convolutional-based MIL strategy. The formulated framework is generic, flexible, scalable and is the first to introduce contextual dependencies between decisions taken at the patch level. It achieved state-of-the-art performance in pan-cancer subtype classification. The code of this work will be made available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge