Solar Flare Index Prediction Using SDO/HMI Vector Magnetic Data Products with Statistical and Machine Learning Methods
Paper and Code
Oct 06, 2022
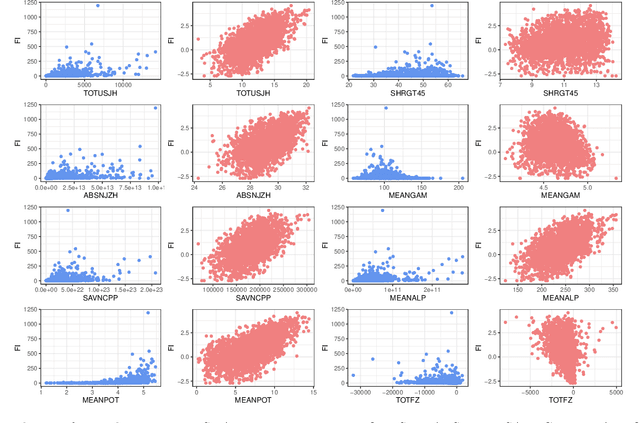
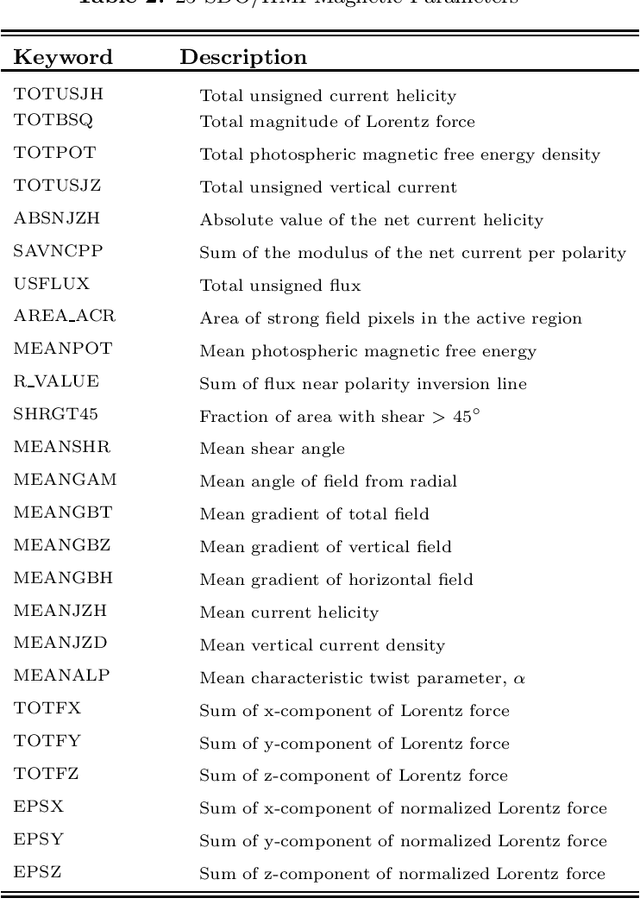
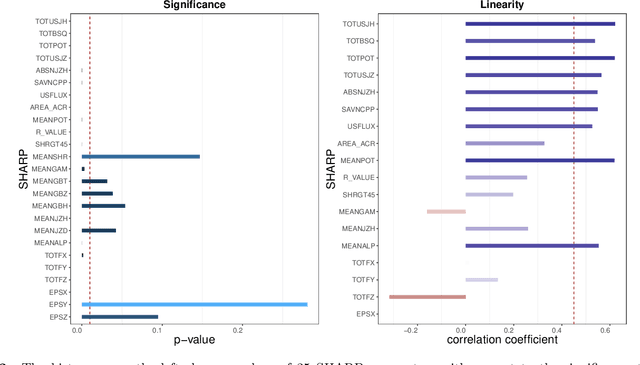
Solar flares, especially the M- and X-class flares, are often associated with coronal mass ejections (CMEs). They are the most important sources of space weather effects, that can severely impact the near-Earth environment. Thus it is essential to forecast flares (especially the M-and X-class ones) to mitigate their destructive and hazardous consequences. Here, we introduce several statistical and Machine Learning approaches to the prediction of the AR's Flare Index (FI) that quantifies the flare productivity of an AR by taking into account the numbers of different class flares within a certain time interval. Specifically, our sample includes 563 ARs appeared on solar disk from May 2010 to Dec 2017. The 25 magnetic parameters, provided by the Space-weather HMI Active Region Patches (SHARP) from Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI) on board the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), characterize coronal magnetic energy stored in ARs by proxy and are used as the predictors. We investigate the relationship between these SHARP parameters and the FI of ARs with a machine-learning algorithm (spline regression) and the resampling method (Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique for Regression with Gaussian Noise, short by SMOGN). Based on the established relationship, we are able to predict the value of FIs for a given AR within the next 1-day period. Compared with other 4 popular machine learning algorithms, our methods improve the accuracy of FI prediction, especially for large FI. In addition, we sort the importance of SHARP parameters by Borda Count method calculated from the ranks that are rendered by 9 different machine learning methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge