Soft-labeling Strategies for Rapid Sub-Typing
Paper and Code
Sep 23, 2022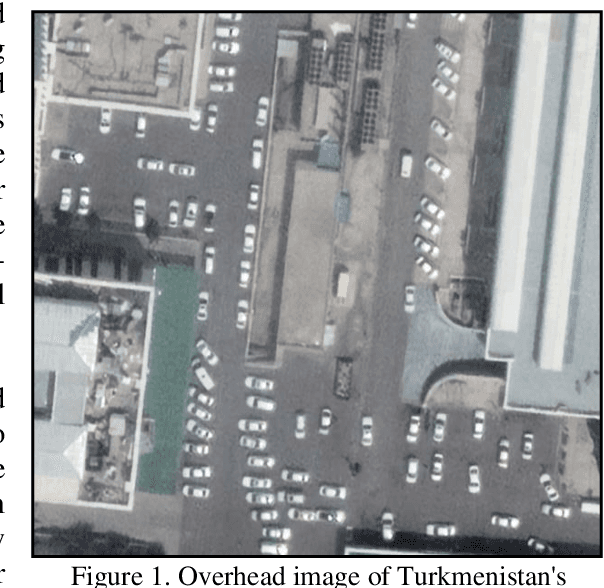
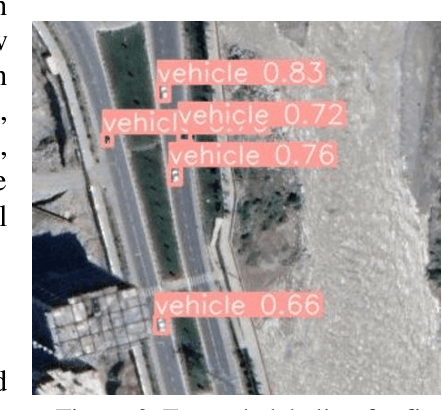

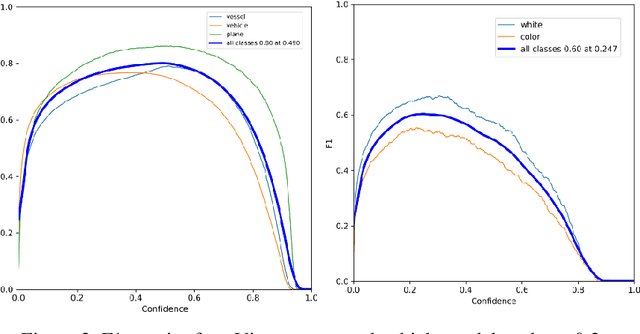
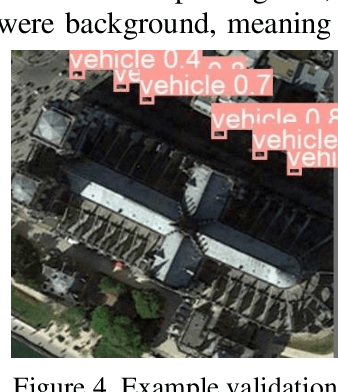
The challenge of labeling large example datasets for computer vision continues to limit the availability and scope of image repositories. This research provides a new method for automated data collection, curation, labeling, and iterative training with minimal human intervention for the case of overhead satellite imagery and object detection. The new operational scale effectively scanned an entire city (68 square miles) in grid search and yielded a prediction of car color from space observations. A partially trained yolov5 model served as an initial inference seed to output further, more refined model predictions in iterative cycles. Soft labeling here refers to accepting label noise as a potentially valuable augmentation to reduce overfitting and enhance generalized predictions to previously unseen test data. The approach takes advantage of a real-world instance where a cropped image of a car can automatically receive sub-type information as white or colorful from pixel values alone, thus completing an end-to-end pipeline without overdependence on human labor.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge