SNAP: Sequential Non-Ancestor Pruning for Targeted Causal Effect Estimation With an Unknown Graph
Paper and Code
Feb 11, 2025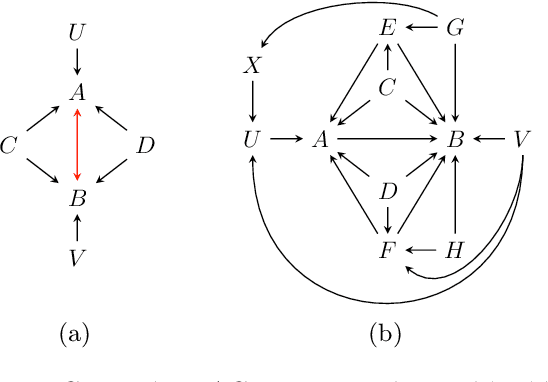
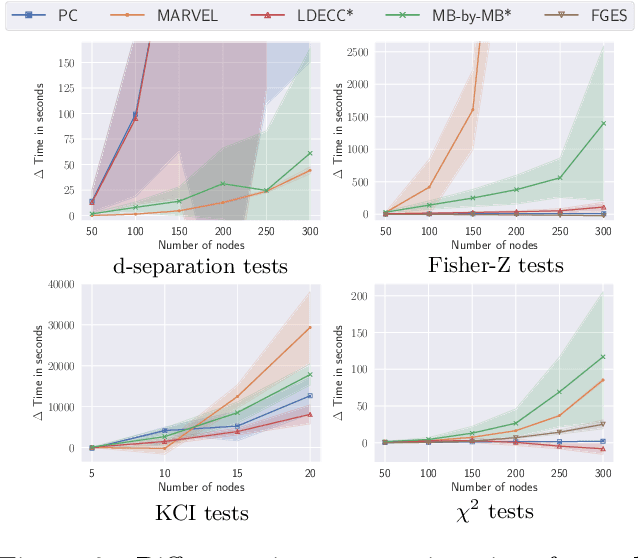
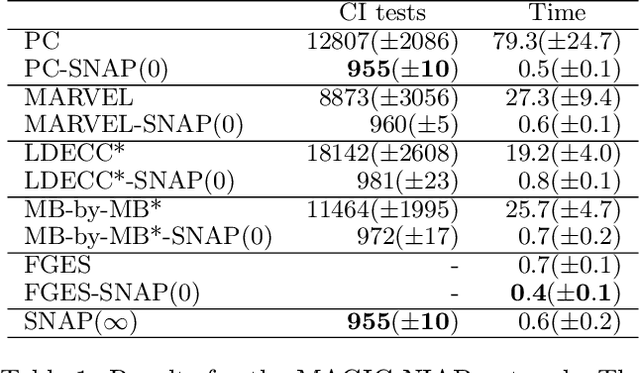
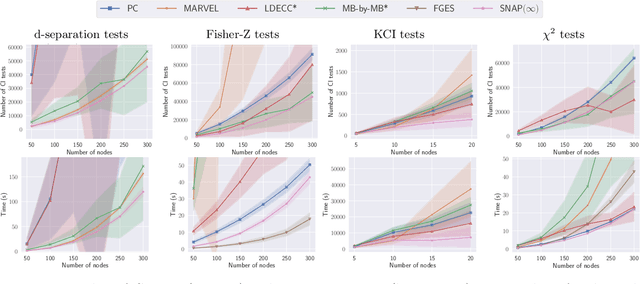
Causal discovery can be computationally demanding for large numbers of variables. If we only wish to estimate the causal effects on a small subset of target variables, we might not need to learn the causal graph for all variables, but only a small subgraph that includes the targets and their adjustment sets. In this paper, we focus on identifying causal effects between target variables in a computationally and statistically efficient way. This task combines causal discovery and effect estimation, aligning the discovery objective with the effects to be estimated. We show that definite non-ancestors of the targets are unnecessary to learn causal relations between the targets and to identify efficient adjustments sets. We sequentially identify and prune these definite non-ancestors with our Sequential Non-Ancestor Pruning (SNAP) framework, which can be used either as a preprocessing step to standard causal discovery methods, or as a standalone sound and complete causal discovery algorithm. Our results on synthetic and real data show that both approaches substantially reduce the number of independence tests and the computation time without compromising the quality of causal effect estimations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge