Simplifying Sentences with Sequence to Sequence Models
Paper and Code
May 15, 2018


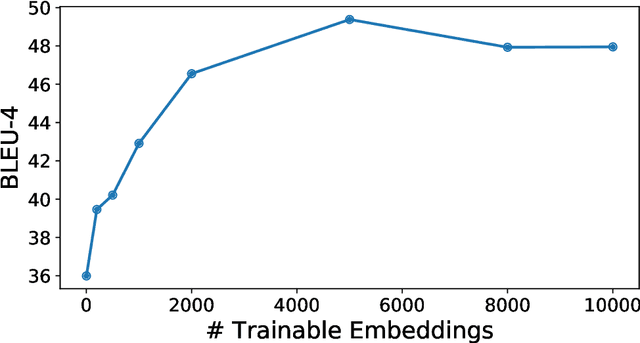
We simplify sentences with an attentive neural network sequence to sequence model, dubbed S4. The model includes a novel word-copy mechanism and loss function to exploit linguistic similarities between the original and simplified sentences. It also jointly uses pre-trained and fine-tuned word embeddings to capture the semantics of complex sentences and to mitigate the effects of limited data. When trained and evaluated on pairs of sentences from thousands of news articles, we observe a 8.8 point improvement in BLEU score over a sequence to sequence baseline; however, learning word substitutions remains difficult. Such sequence to sequence models are promising for other text generation tasks such as style transfer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge