Semi-Supervised Disentanglement of Class-Related and Class-Independent Factors in VAE
Paper and Code
Feb 01, 2021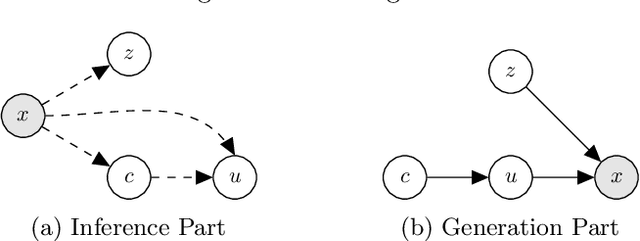
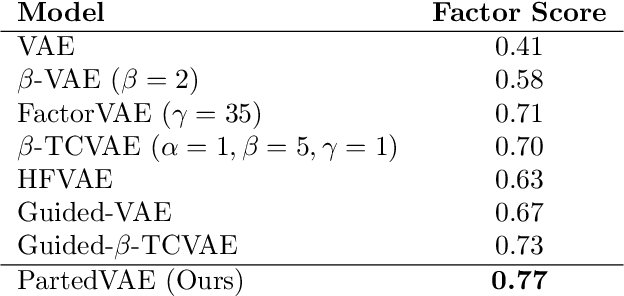
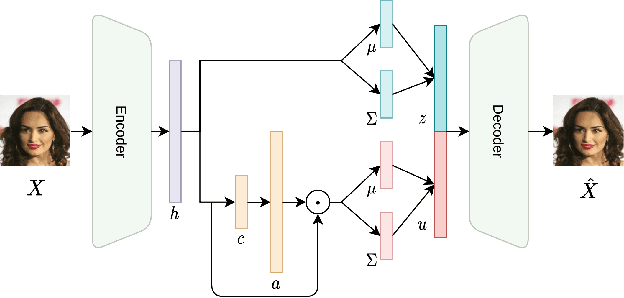
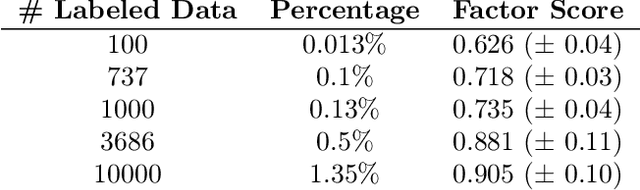
In recent years, extending variational autoencoder's framework to learn disentangled representations has received much attention. We address this problem by proposing a framework capable of disentangling class-related and class-independent factors of variation in data. Our framework employs an attention mechanism in its latent space in order to improve the process of extracting class-related factors from data. We also deal with the multimodality of data distribution by utilizing mixture models as learnable prior distributions, as well as incorporating the Bhattacharyya coefficient in the objective function to prevent highly overlapping mixtures. Our model's encoder is further trained in a semi-supervised manner, with a small fraction of labeled data, to improve representations' interpretability. Experiments show that our framework disentangles class-related and class-independent factors of variation and learns interpretable features. Moreover, we demonstrate our model's performance with quantitative and qualitative results on various datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge