Semi-supervised Deep Learning for Image Classification with Distribution Mismatch: A Survey
Paper and Code
Mar 10, 2022
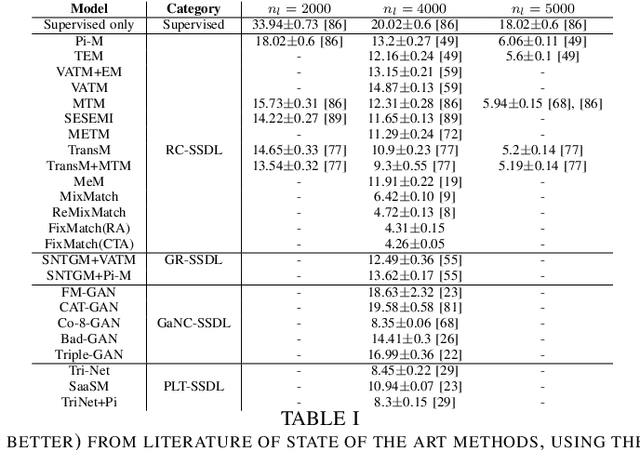
Deep learning methodologies have been employed in several different fields, with an outstanding success in image recognition applications, such as material quality control, medical imaging, autonomous driving, etc. Deep learning models rely on the abundance of labelled observations to train a prospective model. These models are composed of millions of parameters to estimate, increasing the need of more training observations. Frequently it is expensive to gather labelled observations of data, making the usage of deep learning models not ideal, as the model might over-fit data. In a semi-supervised setting, unlabelled data is used to improve the levels of accuracy and generalization of a model with small labelled datasets. Nevertheless, in many situations different unlabelled data sources might be available. This raises the risk of a significant distribution mismatch between the labelled and unlabelled datasets. Such phenomena can cause a considerable performance hit to typical semi-supervised deep learning frameworks, which often assume that both labelled and unlabelled datasets are drawn from similar distributions. Therefore, in this paper we study the latest approaches for semi-supervised deep learning for image recognition. Emphasis is made in semi-supervised deep learning models designed to deal with a distribution mismatch between the labelled and unlabelled datasets. We address open challenges with the aim to encourage the community to tackle them, and overcome the high data demand of traditional deep learning pipelines under real-world usage settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge