Semantic categories of artifacts and animals reflect efficient coding
Paper and Code
May 11, 2019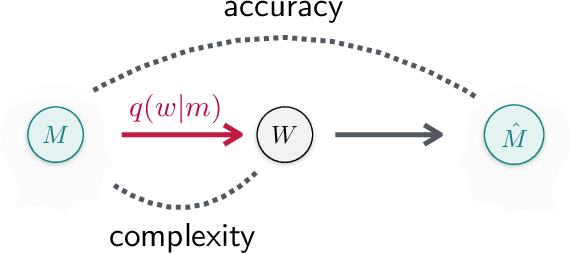
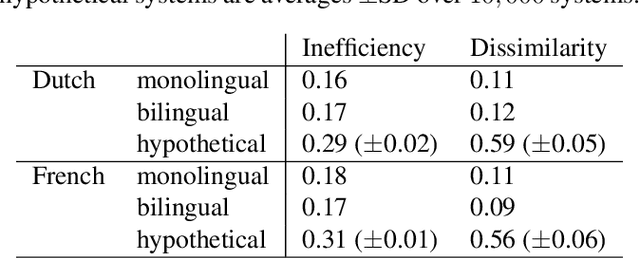
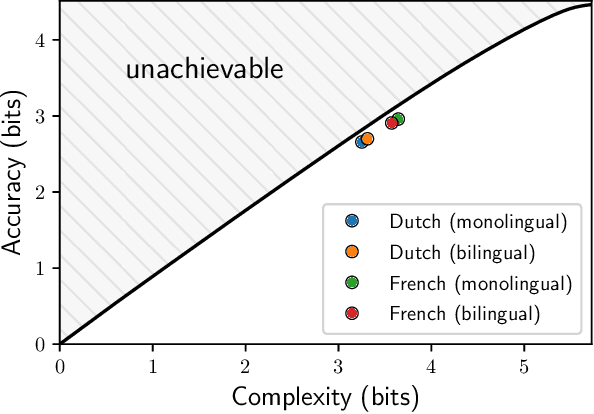
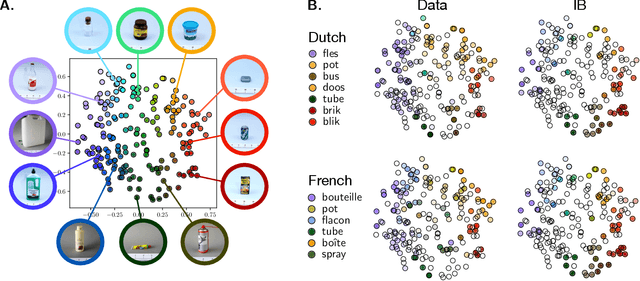
It has been argued that semantic categories across languages reflect pressure for efficient communication. Recently, this idea has been cast in terms of a general information-theoretic principle of efficiency, the Information Bottleneck (IB) principle, and it has been shown that this principle accounts for the emergence and evolution of named color categories across languages, including soft structure and patterns of inconsistent naming. However, it is not yet clear to what extent this account generalizes to semantic domains other than color. Here we show that it generalizes to two qualitatively different semantic domains: names for containers, and for animals. First, we show that container naming in Dutch and French is near-optimal in the IB sense, and that IB broadly accounts for soft categories and inconsistent naming patterns in both languages. Second, we show that a hierarchy of animal categories derived from IB captures cross-linguistic tendencies in the growth of animal taxonomies. Taken together, these findings suggest that fundamental information-theoretic principles of efficient coding may shape semantic categories across languages and across domains.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge